Introduction
- Wash hands (and don PPE if needed)
- Introduce yourself (name and role)
- Confirm patient’s name and DOB
- Explain what the examination involves
- Gain consent to continue
- Expose the patient’s legs from the knee down
- Position the patient standing
- Ask if patient in any pain before continuing
Look
Clinical Signs
- Body habitus
- Scars
- Wasting of muscles
Objects and Equipment
- Walking aids
- Prescriptions
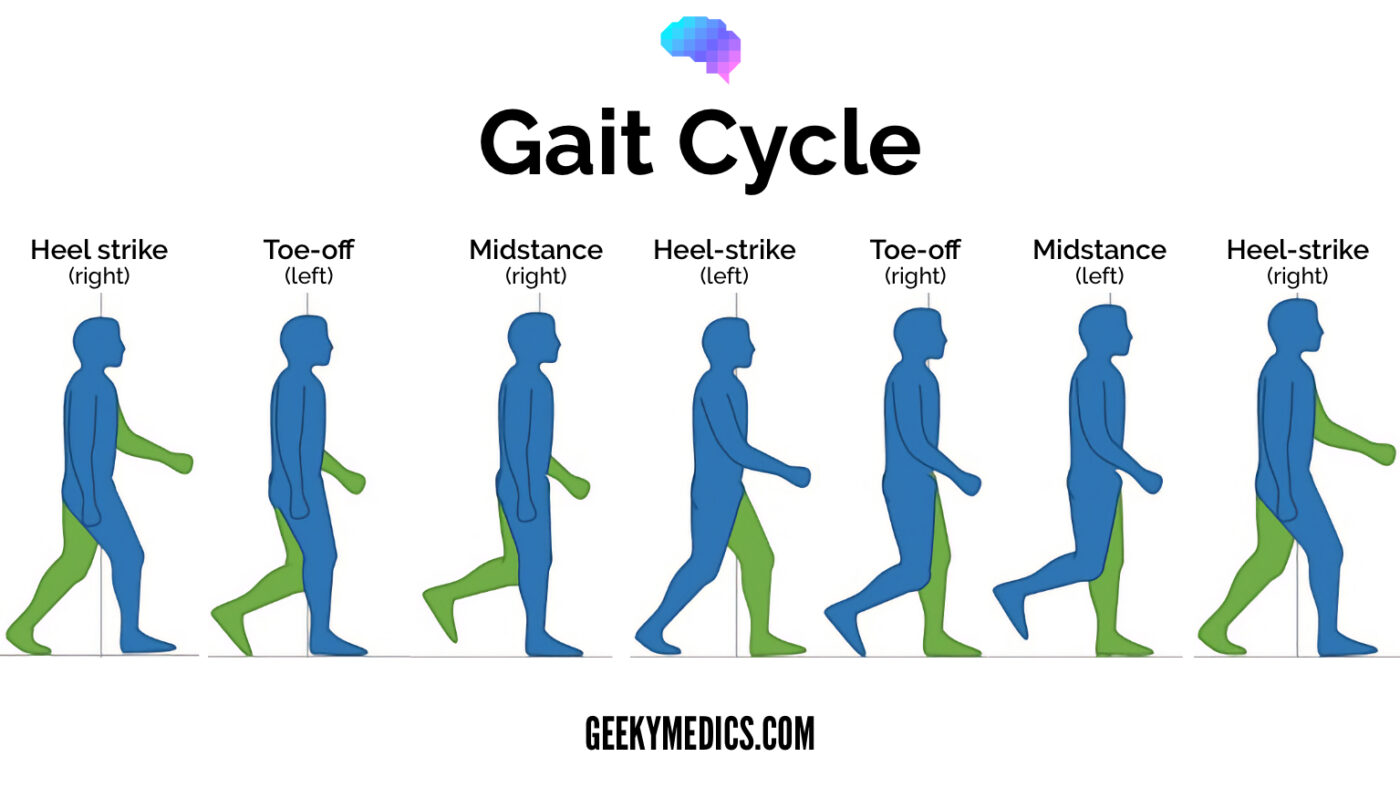
Gait
Ask the patient to walk normally, on heels (arthritis) and tip-toes (muscle weakness). Look for:
- Gait cycle
- ROM
- Limping leg length
- Turning
- Height of steps - high stepping foot drop, peroneal nerve palsy
Closer inspection
- In all planes
- Psoriasis blaques
- Fixed flexion deformities of the toes
- Big toe misalignment
- Calluses
- Foot arch
- Achilles tendon
Feel - 5
Temperature
- Assess and compare
Pulses
- Posterior tibial
- Dorsalis pedis
MTP joint squeeze
- Gently squeeze
- Observe for signs of discomfort
Ankle and foot palpation
- Metatarsal and tarsal bones
- Tarsal joint
- Ankle joint
- Subtalar joint
- Calcaneum
- Medial/lateral malleoli
- Distal fibula
Achilles tendon palpation
- Palpate gastrocnemius muscle and tendon
- Note any tenderness, swelling or discontinuity
Move
Active and passive
- Foot plantar flexion
- Foot dorsiflexion
- Toe flexion
- Toe extension
- Ankle inversion
- Ankle eversion
Passive only
- Subtalar joint
- Midtarsal joint
Special tests
Simmonds’ test
Assessing for Achilles tendon rupture
- Ask the patient to kneel on a chair with their feet handing over the edge
- Squeeze both of the calves in turn
To Complete the Exam
- Explain to the patient that the examination is now finished.
- Thank the patient for their time.
- Dispose of PPE appropriately and wash your hands.
- Summarise your findings.