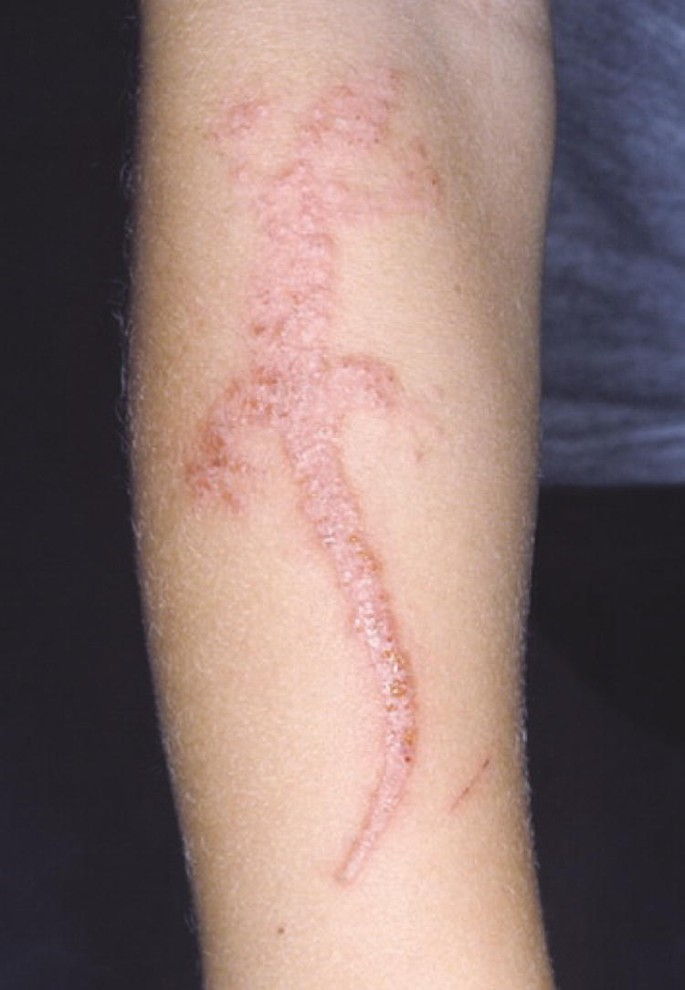
Contact dermatitis is a skin condition characterized by inflammation resulting from direct skin contact with an irritant or allergen. It presents as red, itchy Rashes and can be classified into irritant contact dermatitis (ICD) and allergic contact dermatitis (ACD).
Causes/Factors:
- Irritants: Substances that directly damage the skin, such as soaps, detergents, or chemicals.
- Allergens: Substances that trigger an allergic reaction, such as certain metals, plants, or cosmetics.
Clinical Presentation:
- Redness: Erythema at the contact site.
- Itching: Pruritus is a common symptom.
- Swelling and Blisters: Present in severe cases.
Diagnostic Tests:
- Patch Testing: Identifying specific allergens causing ACD.
- Elimination Diet: In cases of suspected food allergies.
Management:
-
Identify and Remove the Trigger:
- Irritant: Avoid the substance causing irritation.
- Allergen: Identify and eliminate exposure to the allergen.
-
Topical Treatments:
- Corticosteroid Creams or Ointments: Reduce inflammation and itching.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: (e.g., tacrolimus, pimecrolimus) for certain cases.
-
Oral Medications:
- Antihistamines: Relieve itching and reduce allergic reactions.
- Oral Corticosteroids: In severe cases for a short duration.
-
Wet Compresses:
- Applying cool, wet compresses can soothe the affected area.
-
Emollients/Moisturizers:
- Use hypoallergenic moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated.
-
Avoid Scratching:
- Scratching can worsen the condition and lead to infection.
-
Barrier Creams:
- In cases of irritant contact dermatitis, use barrier creams to protect the skin.