Introduction
- Wash hands (and don PPE if needed)
- Introduce yourself (name and role)
- Confirm patient’s name and DOB
- Explain what the examination involves
- Gain consent to continue
- Ask if patient in any pain before continuing
General Observation
-
Conscious level
-
Speech slurring
-
Facial asymmetry
-
Problem with eyelids
-
Obvious limb weakness
-
Walking aids
-
Hearing aids
-
Visual aids
Olfactory Nerve (1)
- Have You Noticed Any Change in Smell?
Optic Nerve (2)
Have you ever had any problems with your vision or noticed any changes?
Do you wear glasses?
Snellen Test
- Ensure that the patient is wearing glasses if normally does so
- Ask patient to cover one eye
- Ensure patient is correct distance (6m effective) away
- Move closer (3m) if unable to read at 6m
Visual Fields
- Ask patient to cover one eye
- Ask patient to let you know when they can see the finger
- Ensure the finger is in the mid line
- Test 4 quadrants of field and repeat on other eye Could also perform visual inattention and blind spot test
Fundoscopy
- Offer to do
- Red reflex - absent may indicate cataract
- Make sure your left eye is looking into their left eye to avoid complete face to face positioning!
- Follow arteries towards the optic disc - they usually branch in a way to form arrow shapes that point towards the optic disc
- Find 4 vessels and look in each quadrant
Check Pupil Size and Alignment
Check Pupillary Reflexes
- Direct and consensual
- Issues with direct reflex - CN2 lesion
- Issues with consensual reflex - CN3 lesion
Accommodation
- Move finger towards nose of patient and watch for eyes - both pupils should constrict as the eyes converge
Say You Would Assess Colour Using Ishihara Chart
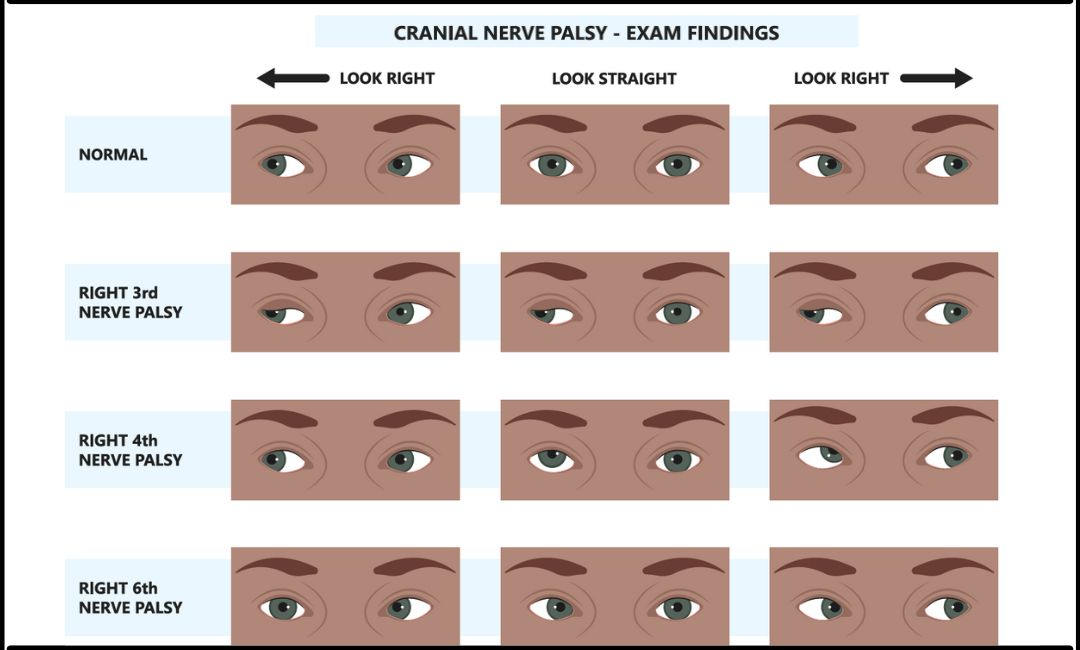
Oculomotor (3), Trochlear (4) and Abducens (6)
H Finger Follow Test
- Ask patient to follow finger for eyes
- On lateral movement go a bit further than what the patient can do and watch for nystagmus
- Eye cannot move in and down - CN4 lesion (superior oblique)
- Eye cannot move laterally - CN6 lesion (lateral rectus)
- Eye cannot move in other directions - CN3 lesions (other intraocular muscles)
Trigeminal (5)
Fine touch Sensation
- Get some cotton wool
- Give patient reference of what it will feel like somewhere other than their face
- Tell them to say when they can feel it
- Test all divisions of trigeminal on both sides
Course touch
- Repeat with a neurotip instead of cotton wool
Assess Muscles of Mastication
- Feel for temporalis & masseter muscles for atrophy
- Ask for jaw to be open and for it to resist closing it
? Corneal reflex
- Small touch on corneal with cotton to elicit blink
- CN 5 afferent CN 7 efferent
? Jaw Jerk
- Ask patient to relax jaw
- Place finger on mentalis muscle and hit with tendon hammer
- Exaggerated jerk is bad usually to side of lesion
Facial Nerve (7)
Facial Expression Assessment
Check for symmetry each time
- Ask patient to raise eyebrows and don’t let me push them down - frontalis
- Scrunch up eyes and don’t let me open them - orbicularis oculi
- Smile and show teeth and then purse lips - orbicularis oris
- Puff out cheek and don’t let me get any air out - buccinators
Vestibulocochlear (8)
Have You Been Hearing Sounds Louder than Usual?
Whispering Hearing Test
Explain to patient that you are going to go behind them and whisper a number and you want them to repeat what they heard
- Assess at 15cm and 60cm
- Test one ear at a time
- Whisper a number and check patient response is the same
Rinne’s Test
To test whether bone conduction is louder than air conduction. Conduct test on both ears
- Ask patient if they can hear the vibrating tuning fork help at the entrance to the ear canal.
- Then place the vibrating fork on the mastoid process
- Then ask which is loudest
In normal hearing the test is positive - and air conduction is louder than bone conduction
Weber’s Test
Used in conjunction with Rinne’s test to rule out unilateral deafness
- Place tuning fork in the centre of the patient’s forehead and ask whether they can hear this equally on both sides or more on one side.
- If its louder in one ear it could mean either an ipsilateral conductive hearing loss or contralateral sensorineural hearing loss
Glossopharyngeal (9)
- Have you experienced any changes in taste?
? Gag reflex
- Offer to do
- Touch posterior pharynx on either side
- CN 9 is afferent CN 10 is efferent
Vagus (10) and Hypoglossal (12)
While you have the light in your hand might as well assess other things that require it
- Ask patient to open their mouth and say ahh - palate should rise equally (vagus) - uvula deviates away from lesions
- Ask patient to stick out their tongue and move side to side (hypoglossal) - deviation towards lesion
Accessory Nerve (11)
Test Power of Shoulder Shrug and Neck Turning
Accessory supplies trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles
End Pieces
- Peripheral nerve exam
- MRI/CT head
- LP
To Complete the Exam
- Explain to the patient that the examination is now finished.
- Thank the patient for their time.
- Dispose of PPE appropriately and wash your hands.
- Summarise your findings.