Separation of the inner neurosensory retina from the underlying retinal pigment epithelium which allows vitreous fluid to accumulate in the sub-retinal space
3 types of retinal detachment:
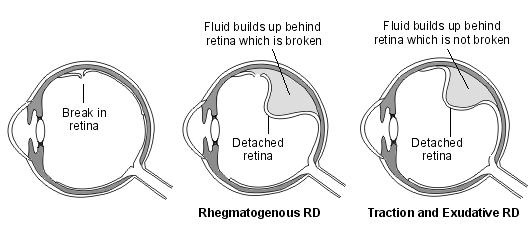
- Rhegmatogenous is most common
- Exudative is caused by leakage of fluid often due to inflammation or malignancy
- Tractional detachment is most commonly seen in people with proliferative Diabetic eye disease - abnormal vasculature causes contraction of the vitreous which then pulls on the underlying retina
Causes/Factors
- M > F
- Myopia
- Family history of retinal break/detachment
- Eye trauma
- Cataract surgery
- Proliferative Diabetic eye disease
Clinical Features
- New onset floaters
- New onset flashes
- Sudden-onset painless and progressive loss of visual fields
- Reduction in visual acuity, blurred or distorted vision
Investigations
- Ophthalmic examination
- Ultrasound
- OCT
Management
Need to reattach the retinal: Arranging immediate referral to an ophthalmologist with retinal surgery expertise to be seen on the same day, if there are symptoms or signs of sight-threatening disease, such as visual field loss or changes in visual acuity, or fundoscopic signs of retinal detachment or vitreous haemorrhage.
- Surgical intervention - pars plana vitrectomy, scleral buckling or pneumatic retinopexy to reattach the retina and seal retinal breaks
- Cryotherapy or Laser photocoagulation to prevent progression of tears to detachment
- Gas or silicone oil tamponade to support reattachment
Complications/red Flags
- Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy (PVR): Development of fibrous membranes on the retinal surface, leading to recurrent detachment.
- Macular Involvement: Detachment involving the macula can result in permanent central vision loss.
- Hypotony: Low intraocular pressure following surgery, leading to potential complications such as choroidal effusion or macular folds.
- Optic Nerve Atrophy: Long-standing retinal detachment can lead to optic nerve damage and irreversible vision loss.