Very treatable condition in those whose conscious level fluctuates and in those having an “evolving Stroke”
Bleeding is from bridging veins between the cortex and venous sinuses that are burst usually due to injury
Causes/Factors
The primary cause of Subdural Hematoma is head trauma, but it can also occur spontaneously or due to bleeding disorders. Common risk factors include:
- Head Injury: Falls, vehicle accidents, and blows to the head.
- Age: Older adults are more prone to SDH due to brain atrophy and thinner blood vessels.
- Alcohol and Drug Use: Substance abuse can increase the risk of trauma and falls.
- Blood-Thinning Medications: Medications like Anticoagulants and antiplatelet drugs can increase the risk of bleeding.
Symptoms
- Fluctuating level of consciousness
- Confusion - altered mental state, memory problems, difficulty concentrating, personality changes
- Headache
Signs
- Seizures
- Unequal pupils
Diagnostic Tests
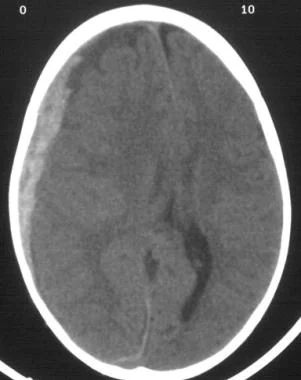
CT/MRI showing:
- Clot
- midline shift (beaware of bilateral isodense clots)
- Look for crescent shaped collection of blood over one hemisphere
Management
- Clotting: Reverse any clotting abnormalities
- Surgery: Larger or symptomatic hematomas may require surgical drainage to relieve pressure on the brain.
- Medications: To control symptoms, manage seizures, and reduce brain swelling.