Two types - ischemia or haemorrhagic
Ischemic - clot blocks supply to distal parts of brain to where that clot got lodged
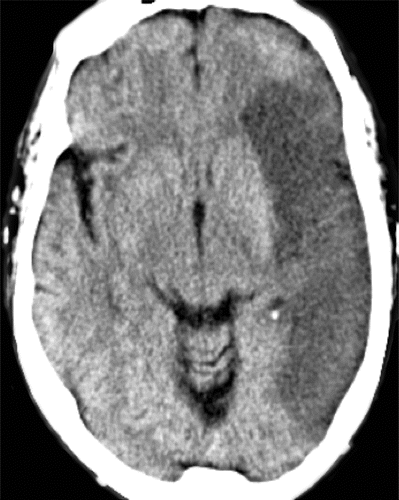
Haemorrhagic - bleeding in the brain causing lack of perfusion (plus irritation to that part of brain)
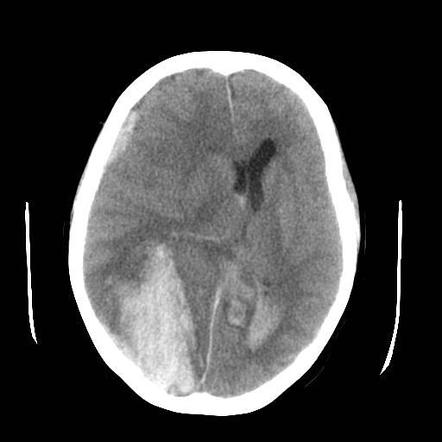
Ischemia can lead to haemorrhagic (haemorrhagic transformation of ischemic stroke )
Causes/Factors
Small vessel occlusion/cerebral microangiopathy or thrombosis
- Cardiac emboli (Atrial Fibrillation)
- Atherothromboembolism (from carotids)
- Aneurism
- CNS bleeds
DDX
- Head injury
- Hypo/hyperglycaemia
- Tumour
- Migraine
Modifiable risk factors
- Hypertension
- Smoking
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Atrial Fibrillation
- PCV (packed cell volume)
- Carotid bruit
- Other substances that affect clotting
Signs
- Sudden onset
- Worst at onset
- Severe headache
- Maybe contralateral or hemiplegia
- face - weakening/drooping
- arms - weakness
- Slurred speech
- 5 syndromes: ataxic hemiparesis, pure motor, pure sensory, sensorimotor and dysarthria/clumsy head
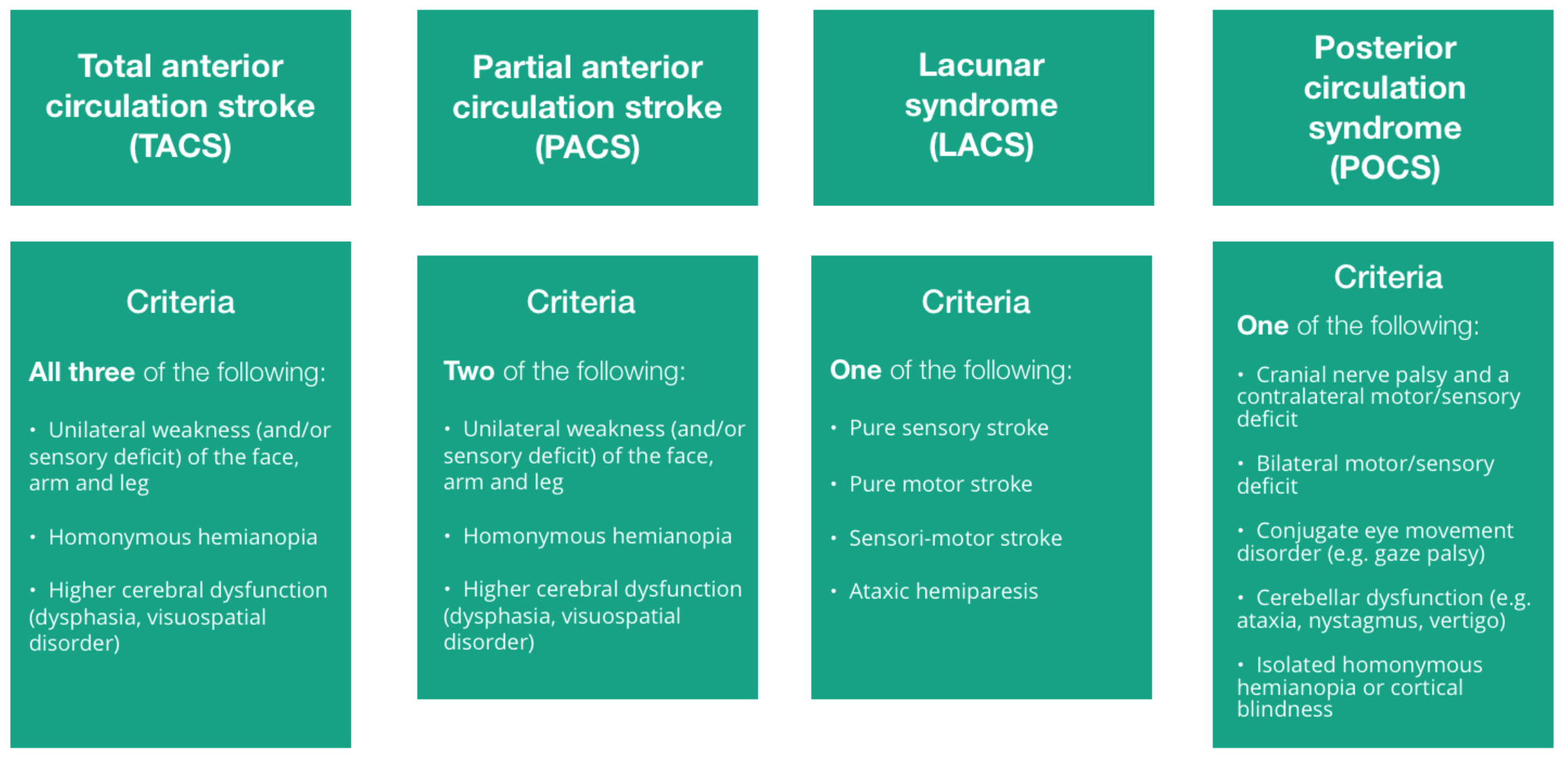
ROSIER - recognition of stroke in the emergencey room
| Symptom | Score |
|---|---|
| LOC/syncope | -1 |
| Seizure activity | -1 |
| Asymmetrical facial weakness | +1 |
| Asymmetrical leg weakness | +1 |
| Speech Disturbance | +1 |
| Visual field defect | +1 |
| >1 stroke possible |
Diagnostic Tests
- CT/MRI rapidly to differentiate between ischemic or haemorrhagic
Looking for source of clot
- Full neuro exam
- ECG to look for AF
- BP for Essential hypertension
- Echo for atherothromboembolism in carotid and AF
- Glucose to rule out hypo/hyperglycaemia
- Any blood issues that cause coagulability, lipid profile, HbA1c, LFT, U&E, CRP, FBC
Management
Exclude Hypoglycaemia Immediate CT brain to exclude haemorrhage Aspirin 300mg daily for two weeks (started after haemorrhage is excluded with a CT) Admission to a specialist stroke centre
Once haemorrhagic excluded:
Aspirin 300mg Stat NG/PO/PR and also PO for 2 weeks then switch to long term antithrombic treatment (e.g. Clopidogrel)
- Within 4.5hrs = thromboctomy + alteplase (thrombolysis)
- Within 6-24hrs = thromboctomy alone
- Wake up stroke (unknown onset) = thromboctomy alone
Chad2Vasc2 score vs ORBIT - no guidelines just clinical judgement
For haemorrhagic confirmed :
- Reverse Anticoagulants if possible (vitamin K for Warfarin, idarucizumab for dabigatran)
- Neurosurgical discussion - coiling (endovascular embolization) can be used to stop further bleeding. Surgery can also be done to remove excess blood and reduce intracranial pressure
Screen swallow - nil by mouth until this is done (keep hydrated)
Rehabilitation
- Swallow test - check for signs of aspiration or voice change
- Falls risk assessment
- Bladder and bowel care
- Physiotherapy - monitor progress
- Monitor mood
- Drugs - High dose statins: 80mg atorvastatin, anticoagulation in AF: DOAC, Anti-platelets, anti-diabetics