Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a complex autoimmune disease that can affect multiple organs and systems in the body. It is a Type III hypersensitivity reaction. SLE varies widely in its presentation and severity.
Anti-DNA reaction so can present in any system
Causes/Factors
Combination of environmental and genetic factors
Symptoms and Signs
Classic differentiating symptoms of SLE
- Joint Pain and Swelling: Arthritis especially in small joints of hand and foot.
- Hair Loss: Thinning or hair loss, often in patches.
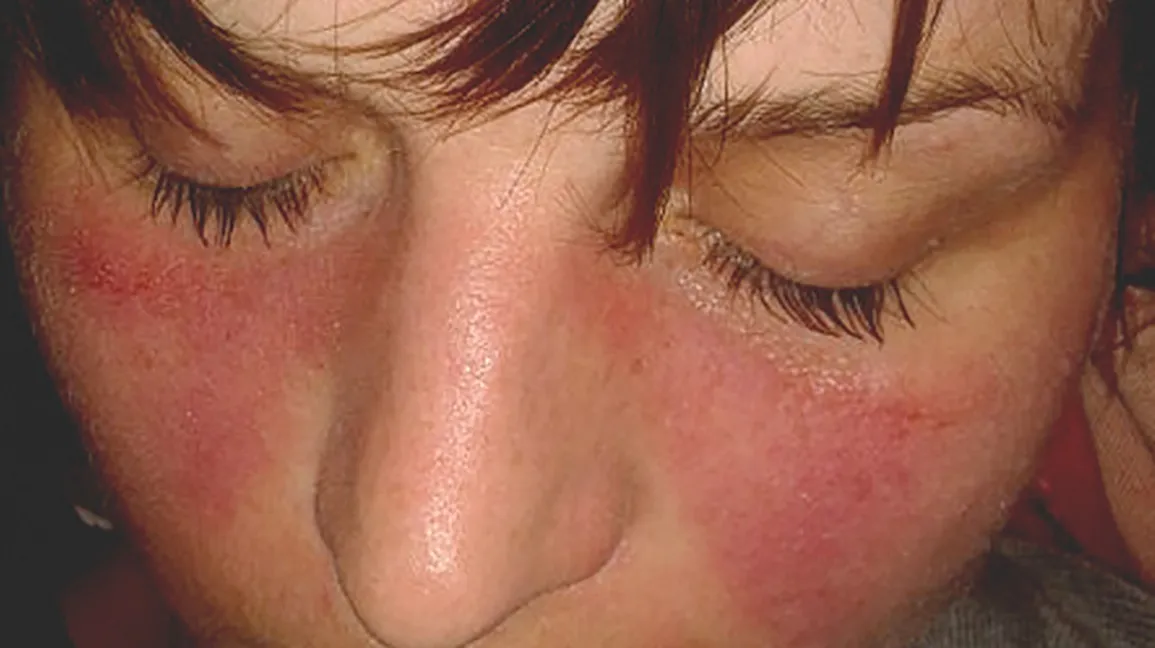
- Malar Rash: Butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and bridge of the nose.
- Mouth Sores: Ulcers in the mouth or nose (esp in odd places, arch of palate)
Other non-specific symptoms
- Fatigue: Profound tiredness and weakness.
- Fever: Elevated body temperature.
- Raynaud’s Phenomenon: Fingers and toes turning white or blue in response to cold or stress.
- Chest Pain: Pleurisy or Pericarditis, inflammation of the lining around the lungs or heart.
- Kidney Problems: Protein or blood in the urine due to kidney inflammation.
- Neurological Symptoms: Headaches, seizures, or cognitive dysfunction.
Diagnostic Tests
Diagnosis of SLE is done on the balance of the patient having a number of key features found in guidelines. A patient does not need to have all of the features to be diagnosed with SLE
- Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) Test: Detects antibodies that attack the nuclei of cells.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): To check for anemia and abnormal white blood cell counts.
- Anti-DNA Antibody Test: Measures antibodies against DNA.
- Other Autoantibody Tests: Including anti-Sm, anti-Ro, and anti-La antibodies.
- Skin and Kidney Biopsies: May be performed to assess tissue damage.
Management
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, antimalarials, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Sun protection, exercise, balanced diet, stress management.
- Pain Relief: Pain medications for joint pain and discomfort.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups to monitor organ involvement and disease activity.
Complications/red Flags
- Organ Damage: SLE can damage the skin, kidneys, heart, lungs, nervous system, and more.
- Flares: Periods of increased disease activity and symptoms.
- Infections: Weakened immune system can lead to infections.
- Pregnancy Complications: High-risk pregnancies due to increased disease activity.