Loss of protein in urine
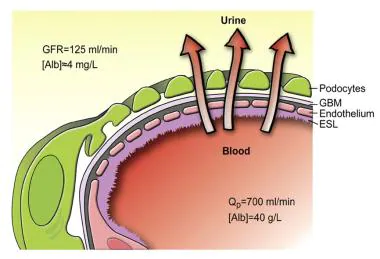 GBM has negative charge to repel proteins
GBM has negative charge to repel proteins
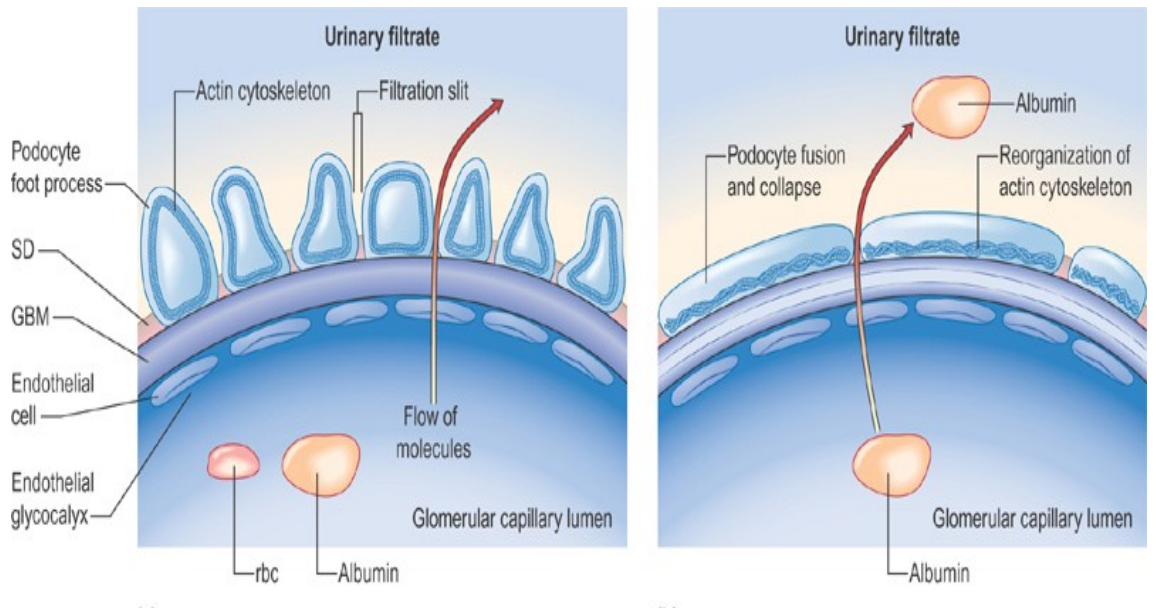 (Left) Loss of negative charge
(Left) Loss of negative charge
Causes/Factors
-
Minimal change disease - most common cause in children. Usually idiopathic and treated with steroids
-
Membranous nephropathy - most common cause in adults
-
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis - most common cause in adults
-
Amyloid
-
HIV, HEP B&C, malaria
-
NSAIDs
Tip
Minimal change disease often comes up in exams. If there’s a 2-5 year old child with oedema proteinuria and low albumin the diagnosis is likely nephrotic syndrome.
Symptoms
-
Proteinuria
-
Hypoalbuminaemia
-
Oedema - ankles, feet, eyes (in severe)
-
Hypercholesterolaemia
Signs
- Peripheral oedema
- Frothy urine
- Weight gain
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
Diagnostic Tests
- Urinalysis
- Blood tests
- Biopsy
Management
Specific
-
Steroids
-
Cyclophosphamide, tacrolimus
-
Loop diuretics Furosemide
-
BP control - ACEi
-
Hypercholesterolaemia - statins
-
Thrombo-prophylaxis - herparin
Complications/red Flags
- Thrombosis - due to loss of blood blotting proteins
- High blood cholesterol and elevated blood triglycerides - live makes more albumin along with cholesterol and triglycerides
- Poor nutrition - loss of blood protein
- High BP
- Acute Kidney Injury
- Chronic Kidney Disease
- Infections