aka rodent ulcer
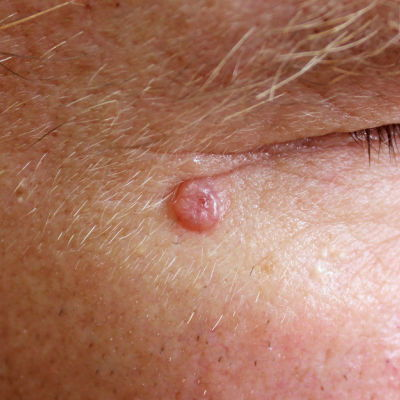 Nodular BCC
Nodular BCC
Causes/Factors
The primary cause is prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. Other risk factors include:
- Fair Skin: Light-skinned individuals are more susceptible.
- Chronic Sun Exposure: Especially without adequate sun protection.
- History of Skin Cancer: Previous BCCs or other skin cancers increase the risk.
- Immunosuppression: Weakened immune system due to conditions or medications.
- Age: BCC is more common in older adults.
Symptoms
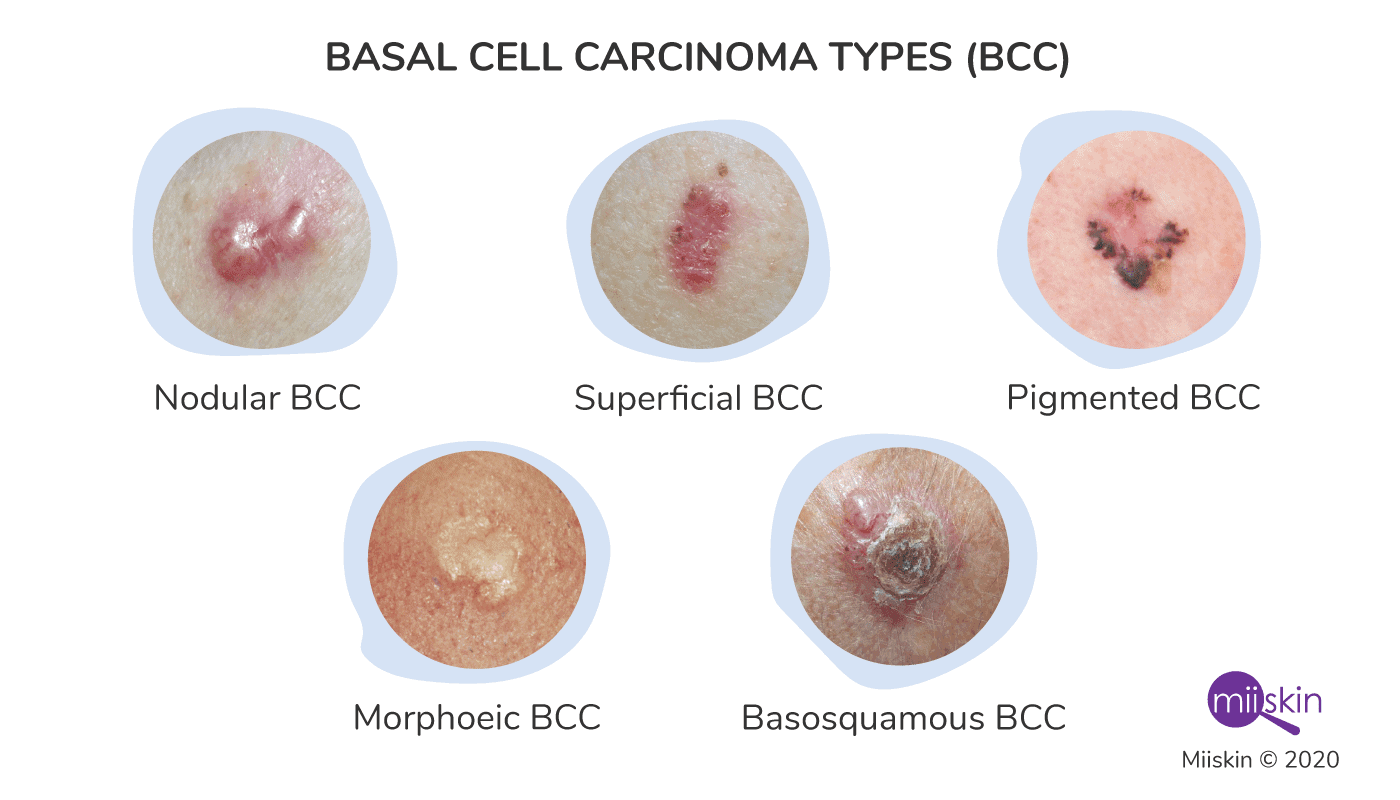
- Nodular BCC: typically a pearly nodule with rolled edge on face or sun-exposed site. May have a central ulcer
- Superficial BCC: lesions appear as red scaly plaques with raised smooth edge. Often on trunk or shoulders.
Diagnostic Tests
- Referral to a dermatologist for input
- Skin biopsy
Management
- Excision
- Cryotherapy
- For topical BCC: flurouracil (efudex) or imiquimod
Complications/red Flags
- Local Tissue Destruction: If left untreated, BCC can invade surrounding tissues and structures.
- Disfigurement: Lesions on the face can cause disfigurement if not properly treated.
- Recurrence: BCCs may recur, especially if not completely removed.