Small bowel obstruction is more common
Results in a build up gas and faecal matter proximal to the obstruction - back pressure
Rest of GI tract secretes fluid that is later absorbed in colon. When there is an obstruction fluid loss from this leads to hypovolaemia and shock.
Causes/Factors
| Common | Rare |
|---|---|
| Hernias *(small bowel) | Strictures (Crohn’s Disease) |
| Adhesions *(small bowel - past surgery) | Intussusception (in young children) |
| Malignancy *(large bowel) | Volvulus (large bowel) |
| Constipation | Gallstone Ileus |
| *big three |
Closed-loop obstruction
- Two points of obstruction in the bowel
- Middle section sandwiched between two points
Might occur with:
- Adhesions
- Hernias
- Volvulus
- A single point of obstruction but with a ileocaecal valve that is competent
Presentation
- Vomiting (particularly green bilious)
- Abdo distension
- Diffuse abdo pain
- Absolute constipation and lack of flactulence
- “Tinkling” bowel sounds may be heard in early obstruction
Investigations
- Abdo XR
- Large bowel touch the peripheries and have lines that do not go completely across the bowel (haustra)
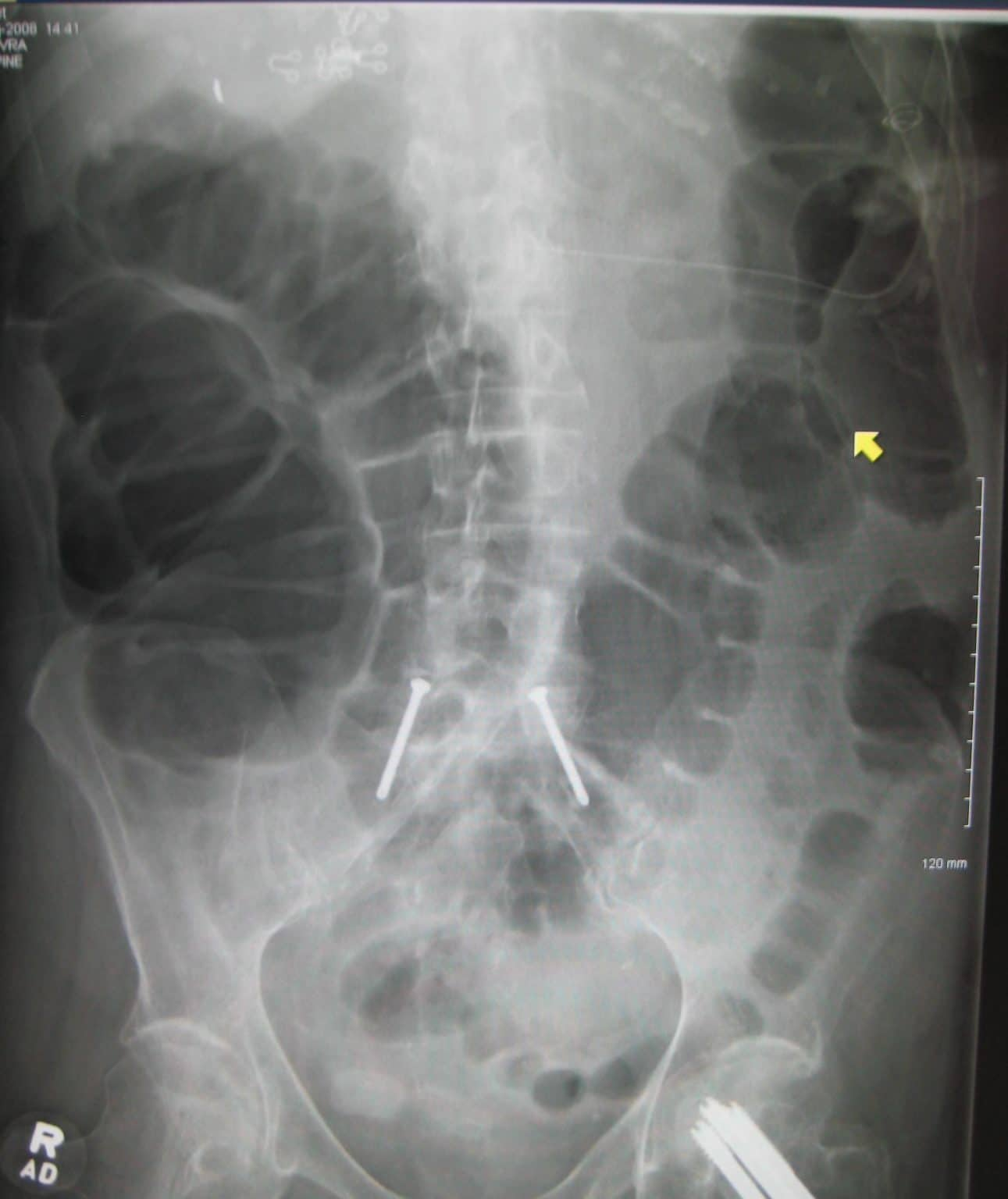
- Small bowel usually don’t extend to the peripheries but have lines that do extend the full length (valvulae conniventes)
- Erect chest XR - to check for pneumoperitoneum (bowel perforation)
Small Bowel Obstruction (coiled-spring appearance)
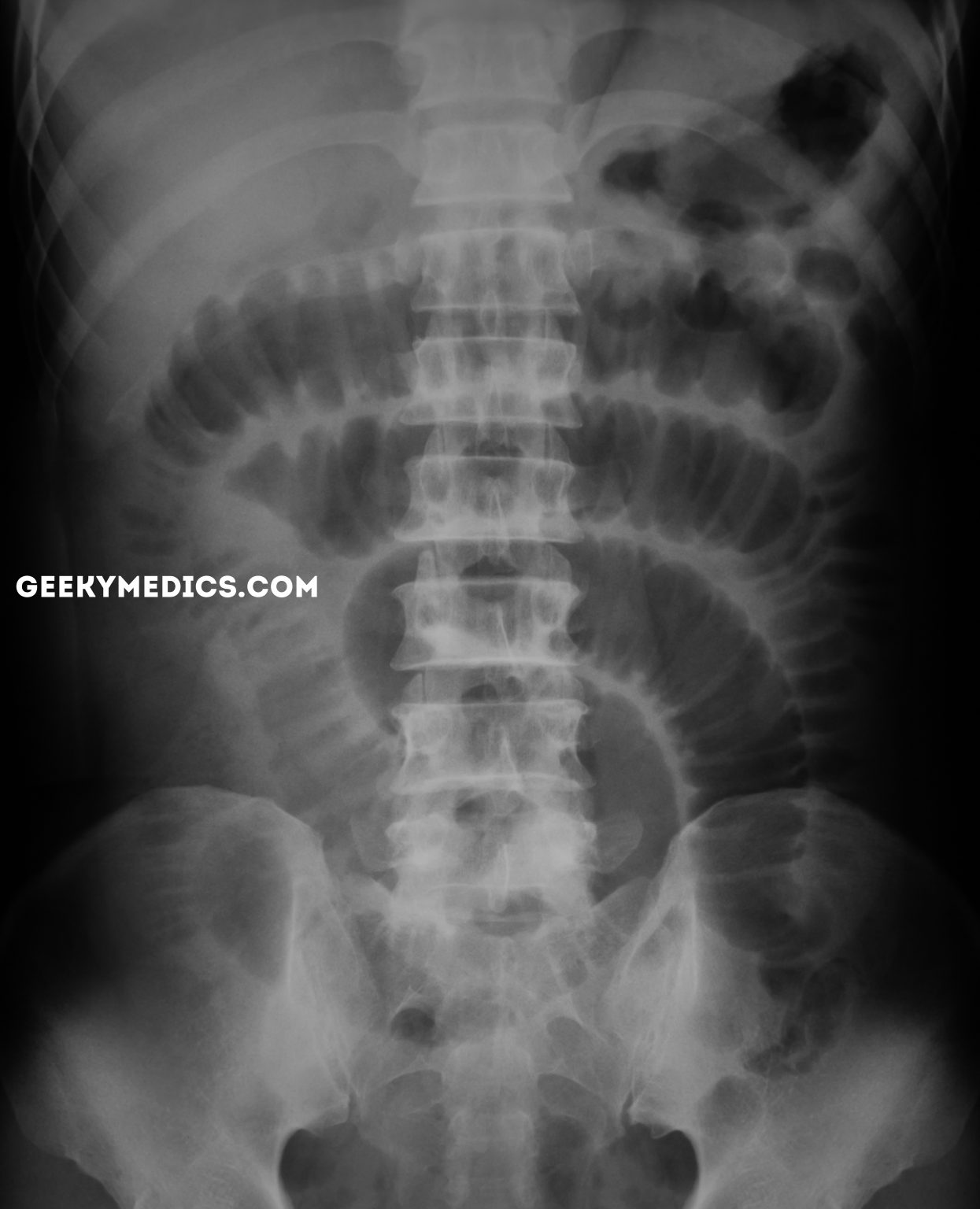
Large Bowel Obstruction
Management
ABCDE approach - may be haemodynamically unstable and require urgent intervention if develop:
- hypovolaemic shock
- Bowel ischaemia
- Bowel perforation
- Sepsis
Full set of bloods:
- U&E
- Metabolic acidosis due to vomiting (VBG)
- Raised lactate due to bowel ischaemia (VBG)
“Drip and suck” management
- Nil by mouth
- IV fluids - to rehydrate and correct electrolyte imbalances
- NG tube with free drainage to allow stomach contents freely drain and reduce risk of vomiting and aspiration
Surgical intervention
Conservative management may be used in first instance in stable patients with obstruction secondary to adhesions or volvulus.
The definitive management is surgery -
- Exploratory surgery - if unclear cause
- Adhesiolysis to treat adhesions
- Hernia repair
- Emergency resection of obstructing tumour
Stents may be inserted during a colonoscopy in obstruction due to a tumour
Complications/red Flags
bad