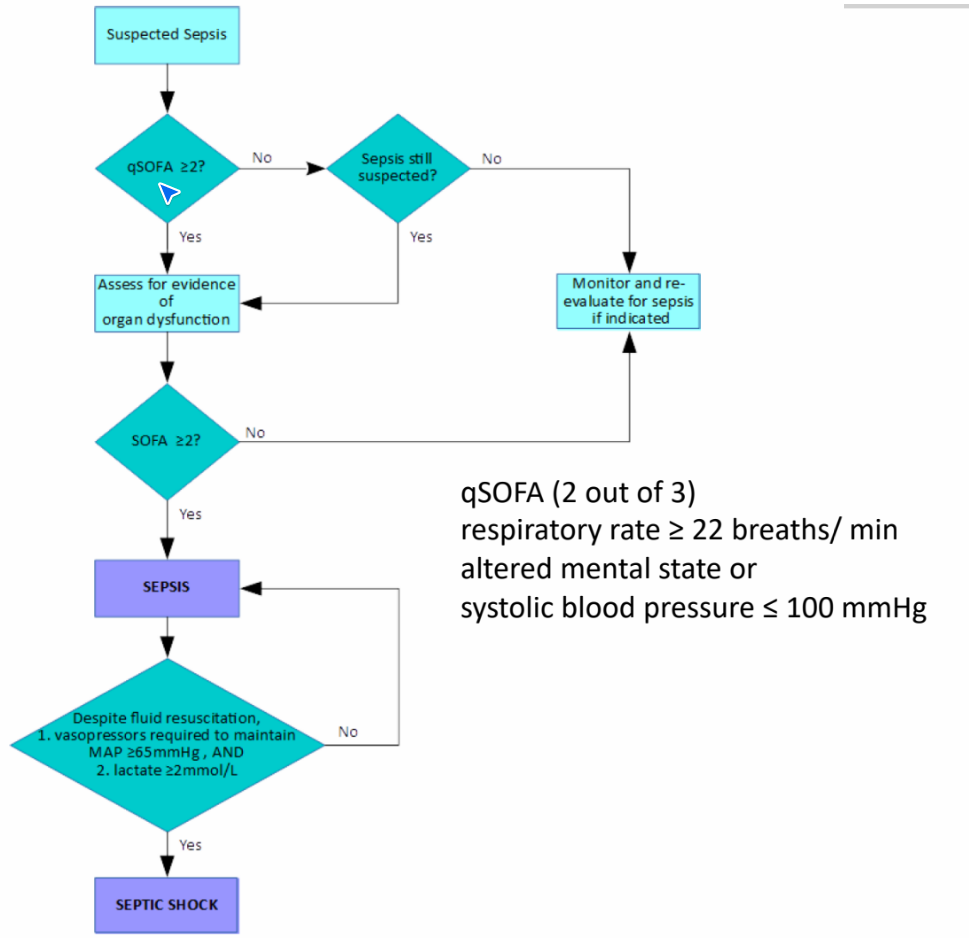
A life threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection
Utilises Quick SODA (qSOFA) scoring system - based on
- RR
- altered mental state
- systolic BP
Septic shock is a subset of sepsis. Profound circulatory, cellular and metabolic abnormalities
- Vasopressor requirement to maintain a MAP >65
- serum lactate level >2mmol/L
Causes/Factors
- < 1 year and > 75 years
- very frail people
- recent trauma or surgery or invasive procedure
- within 6 weeks
- impaired immunity due to
- illness or
- drugs
- steroids, chemotherapy or immunosuppressants
- indwelling lines / catheters
- intravenous drug misusers
- any breach of skin integrity
- cuts, burns, blisters or skin infections
Recognition
- Signs + symptoms of infection
- Be aware that people may have non-specific symptoms
- Pay particular attention to concerns expressed by the person/family
- High NEWS2 score
High Risk Criteria
- Altered mental status
- RR >25
- New need for Oxygen
- HR >130
- Systolic <90 or 40 below normal
- Not passed urine in pervious 18 hours
- Mottled or ashen appearance
- Cyanosis
- Non-blanching rash
Diagnostic Tests
- FBC, CRP, U&E, urine culture, blood culture
- ABG or VBG
- Blood sugar
Management
- Prompt management within 1 hour
- Sepsis6
BUFALO
- Blood cultures and septic screen
- Urine output - monitor hourly
- U&Es urine culture
- Fluid resuscitation
- as clinically indicated
- Antibiotics IV - LTHT guidelines (tazocin? 4.5 g every 8 hours; increased if necessary to 4.5 g every 6 hours)
- Lactate measurement - from arterial or venous blood gas
- Oxygen to correct hypoxia
Hypovolaemia can be
- True hypovolaemia - when the rate of fluid loss exceeds net intake
- Haemorrhage
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Relative hypovolaemia - when there is a decrease in the effect circulating volume
- Sepsis - vasodilation