When too much cortisol is present.
Can cause a hypokalaemic metabolic alkalosis
Cushing’s Disease
Pituitary adenoma releasing ACTH cortisol release
Cushing’s Syndrome
- Any other cause - steroids, adrenal cortex tumour, ectopic tumour eg small cell lung carcinoma
Causes/Factors
CAPE Cushings disease - pituitary adenoma Adrenal adenoma Paraneoplastic syndrome from: carcinoid tumours in lung, small cell carcinoma, islet cell tumours, medullary carcinoma, tumours of thymus gland Exogenous steroids- most common
Peak incidence age 25-40
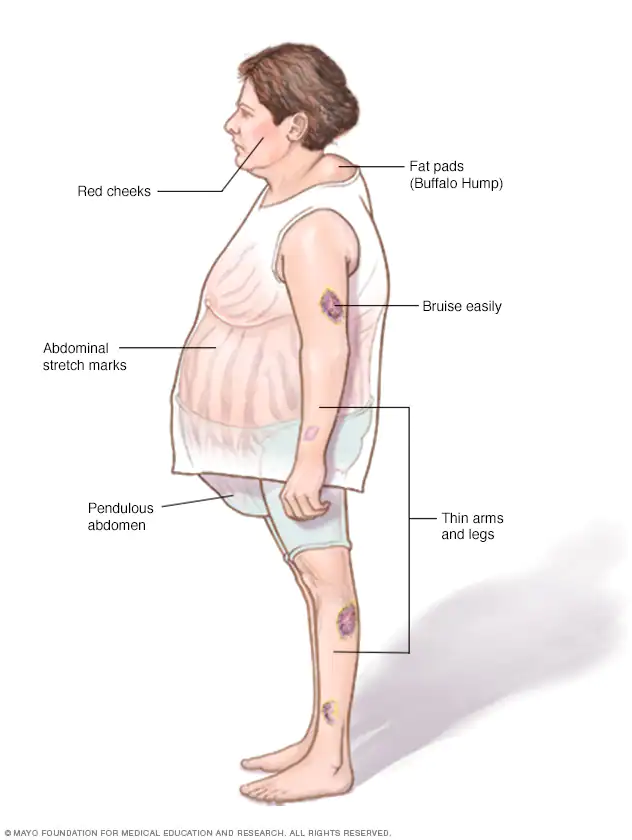
Symptoms
- Weight gain (abdo and face)
- High blood pressure
- Skin changes - fragile with stretch marks
- Mood changes - irritability & anxiety
- osteoporosis
- Menstrual irregularities
- Hirsutism
- Glucose intolerance
Signs
Diagnostic Tests
- Dexamethasone suppression test - synthetic cortisol should suppress cortisol levels
- 24hr urine cortisol test - measures cortisol levels
- Late-night salivary cortisol test
Management
- Surgical removal of tumours
- Medication adjustment - if Cushings via chronic steroid use
- Lifestyle management - weight, BP and glucose
Complications/red Flags
- osteoporosis
- Suppressed immune function increased infection risk
- Cardiovascular complications - due to the high blood pressure