Introduction
- Wash hands (and don PPE if needed)
- Introduce yourself (name and role)
- Confirm patient’s name and DOB
- Explain what the examination involves
- Gain consent to continue
- Expose the upper limbs and position the patient standing
- Ask if patient in any pain before continuing
Look
Clinical Signs
- Scars
- Muscle wasting
Objects and Equipment
- Aids and adaptations
- Prescriptions
Elbow Joint Close Inspection
Look at the elbow in all planes
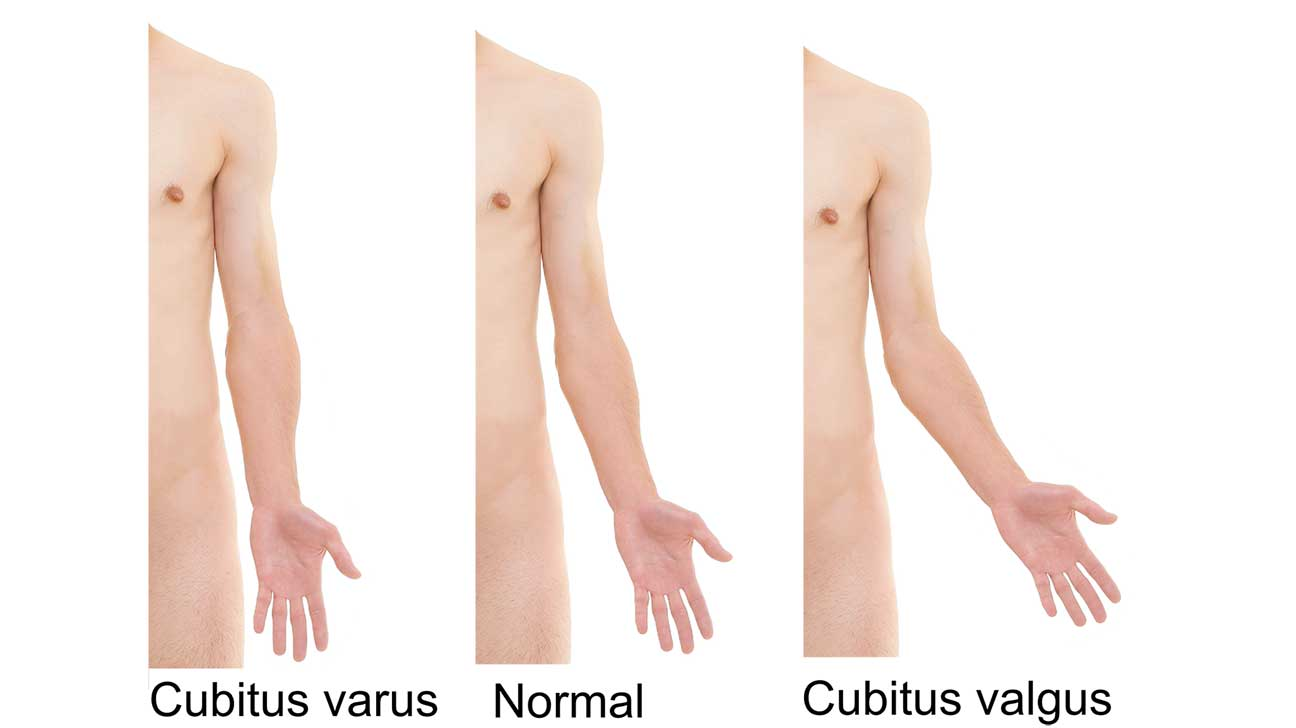
- Carrying angle - cubitus valgus 5-15 is normal
- Scaring
- Bruising
- Swelling
- Abnormal bony prominence
- Dermatology findings
Feel
Temperature
- Assess and compare temperature to either side
Elbow joint palpation
- Radial head
- Radiocapitellar joint
- Lateral and medial epicondyle
- Olecranon
Biceps tendon palpation
- Ask the patient to actively flex their elbow
- Palpate and feel the biceps tendon
Move
Active movement
- Flexion
- Extension
- Pronation
- Supination
Passive movement
- Repeat above movements
- Feel for crepitus
Special tests
Medial epicondylitis (golfer’s elbow)
Inflammation of the flexor tendons at insertion secondary to overload injury. Perform active wrist flexsion against resitance
- Seat the patient and ask them to flex their elbow to 90
- Palpate the medial epicondyle with fingers
- Holds the patients wrist in the other hand
- Ask the patient to make a fist and flex their wrist
Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow)
Same as medial but for extensor tendons
- Seat the patient and ask them to flex their elbow to 90
- Palpate the lateral epicondyle with fingers
- Holds the patients wrist in the other hand
- Ask the patient to make a fist and extend their wrist
To Complete the Exam
- Explain to the patient that the examination is now finished.
- Thank the patient for their time.
- Dispose of PPE appropriately and wash your hands.
- Summarise your findings.
Further Assessments and Investigations
- Shoulder Exam and Wrist Exam
- Upper and Lower Limb Neurological Exam
- Further imaging as required