Introduction
- Wash hands (and don PPE if needed)
- Introduce yourself (name and role)
- Confirm patient’s name and DOB
- Explain what the examination involves
- Gain consent to continue
- Ask if patient in any pain before continuing
Look
Clinical Signs
- Scars
- Wasting of muscles
Objects and Equipment
- Aids and adaptations - wrist splints
- Prescriptions
Hand Inspection
Dorsal aspect
- Hand posture
- Scars, welling, bruising
- Bouchard’s and Heberden’s nodes - occur at PIPJ and DIPJ respectively and are associated with Osteoarthritis
- Swan neck deformity and Z-thumb- RA
- Skin thinning - steroids
- Psoriatic plaques - increased risk of psoriatic arthritis
- Splinter haemorrhages - Infective endocarditis, Sepsis, Vasculitis
- Nail pitting and onycholysis
Palmar aspect of hand
- Hand posture
- Scars
- Swelling
- Dupuytren’s contracture - thickening of the palmar fascia
- Thenar/hypothenar wasting. Isolated wasting of the thenar eminence is suggestive of median nerve damage - carpal tunnel syndrome
- Elbows
- Janeway lesions and Osler’s nodes
Feel
Palms up - 5 in each
Temperature
- Assess and compare
Radial and ulnar pulse
- Palpate to confirm adequate blood supply
Thenar and hypothenar eminence bulk
- Palpate muscle bulk
- Wasting can be caused by disuse atrophy and LMN lesions (eg ulnar and median nerve)
Palmar thickening
- Palpate the palm and detect thickened palmar fascia
Median and ulnar nerve sensation
- Assess median nerve sensation over the thenar eminence and index finger
- Assess ulnar nerve sensation over hypothenar eminence and little finger
Palms down - 5
Radial nerve sensation
- Assess over first dorsal webspace
Temperature
- Cause I’m sure it’ll be really different on this side
MCP joint squeeze
- Gently squeeze across MCP joints
- Observe for signs of discomfort arthropathy
Joint palpation
- Metacarpophalangeal joint
- PIPJ
- DIPJ
- Carpometacarpal joint of the thumb
Palpate extras
Anatomical snuffbox
- Palpate for evidence of scaphoid fracture
- MOI: Fall on an outstretched hand (FOSH)
- Avascular necrosis of scaphoid is risk
Wrist palpation
- Joint lines and any tenderness
Elbow palpation
- Palpate arm along ulnar border to elbow and note tenderness
Move
Active movement
- Finger extension - open and splay fingers
- Finger flexion - make a fist
- Wrist extension
- Wrist flexion
Passive movement
- Repeat above passively and try to feel for creps
Motor assessment
Screens for motor function of radial and median nerve
Wrist and finger extension against resistance
- Wrists back against resistance of wrist and fingers
- Radial nerve
Index finger abduction against resistance
- Splay fingers and stop your from pushing their fingers together
- First dorsal interosseous - ulnar nerve
Thumb abduction against resistance
- Point thumbs to ceiling and don’t let me push down
- Abductor pollicis brevis - median nerve
Function
Assess the hand function with the following tests
- Power grip - squeeze fingers
- Pincer grip - squeeze finger between thumb and index
- Pick up a small object - pick a coin off the table
Special tests
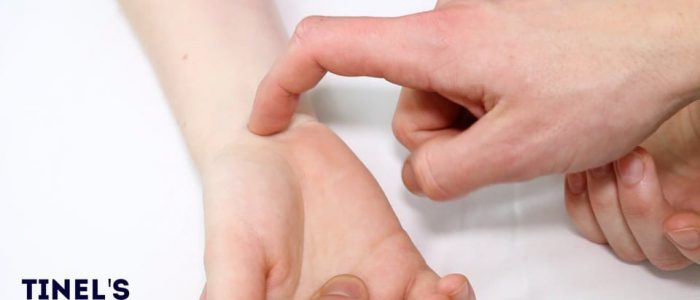
Tinel’s test
Used to identify median nerve compression - carpan tunnel syndrome
- Tap over the carpal tunnel with finger
- If patient has tingling in the thumb and radial two and a half fingers - suggestive of median nerve compression
Phalen’s test
Further for carpal tunnel syndrome
- Ask the patient to hold their wrist in maximum forced flexion for 60 seconds
- If the symptoms of carpal tunnel are reproduced then the test is positive

To Complete the Exam
- Explain to the patient that the examination is now finished.
- Thank the patient for their time.
- Dispose of PPE appropriately and wash your hands.
- Summarise your findings.
Further Assessments and Investigations
- Shoulder Exam and Elbow Exam
- Upper and Lower Limb Neurological Exam
- Further imaging as required