Usually the lining of the joint that gets affected Anyone at any age can get inflammatory arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
^ab6a7d A systemic autoimmune disorder affecting synovial joint membrane with extra-articular manifestations
- Autoimmune
- Most common presents at 40-60s y/o
- 3:1 F:M
- Other organs can be effected
- 80% positive Rheumatoid Factor blood test
- Positive anti-CCP antibody
Signs
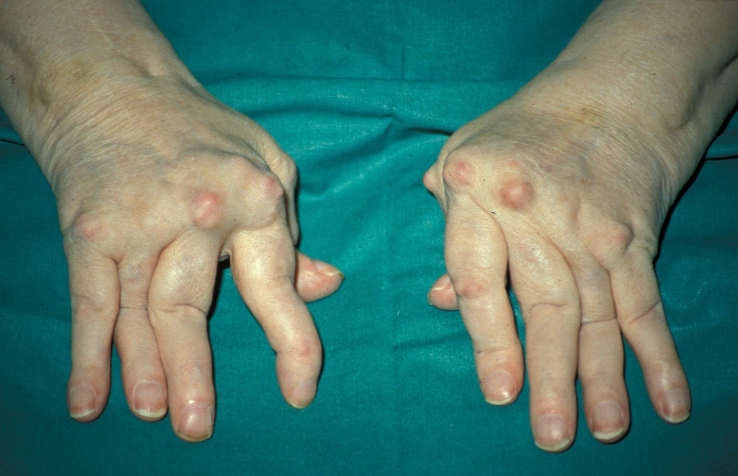
- Symmetrical polyarthritis - most common joints: MCP, wrist, PIP, knee, MTP, shoulder, ankle, C-spine, hip, elbow, TMJ
- Rheumatoid nodules (elbow and lungs)
Symptoms
- Inflammation with swelling, tenderness, warmth and decreased ROM.
- Worse in the morning - improved with movement
Extra-articular:
- Generalised malaise, fatigue
- Pericardtis or percardial effusion
- Vasculitis
- Pulmonary Fibrosis
LESS
- Loss of joint space
- Erosions
- Soft tissue swelling
- Soft bones (osteopaenia)
Diagnostic Tests
- Bloods - ESR, CRP - FBC: Anaemia of chronic disease, thrombocytosis, leukocytosis
- Anti-CCP antibody - more specific and sensitive than RF
- XR/MRI of the area looking for erosions and damage
- Joint aspirations - synovial fluid with increased WCC and protein
Management
- Methotrexate ± steroids
- Can add - sulfasalazine or leflunomide
- If not managed by these switch to TNF-A blocker
Biological therapy
TNF inhibitors eg adalimimab and immunomodulators such as rituximab are used in adults with highly active disease who have failed to respond to 2 DMARDs
Psoriatic Arthritis
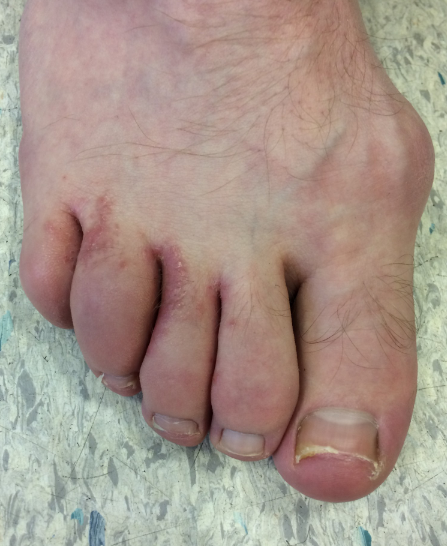
- About 15% of people with Psoriasis will develop psoriatic arthritis
- Dactylitis & nail changes (onycholysis)
- Increased CV risk
Axial Spondylarthritis
- Inflammatory back pain
- Young people
- Can cause red inflamed eyes (Uveitis)
- Untreated bones can fuse and cause an immobile spine