Terminology
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Abscess | local accumulation of pus |
| Bulla | raised circumscribed lesion >5mm containing serous fluid (blister) above the dermis |
| Comedone | plug of dead epithelial material blocking pore: open (blackhead) or closed (whitehead) |
| Erythema | blanchable redness of the skin that can be localised or generalised (dilation of BVs and capillaries) |
| Excoriation | scratch which has broken the surface of skin |
| Lichenification | skin thickening with exaggerated skin markings as a result of repeated rubbing |
| Macule | flat well-defined area of altered skin pigmentation. Areas >10mm are described as patches |
| Nodule | solid, palpable usually subcutaneous lesion >5mm |
| Papule | raised well defined lesion <5mm |
| Plaque | raised flat-topped lesion >20mm |
| Purpura | non blanching violaceous (purplish) discolouration of the skin due to blood that has extravasated from BVs |
| Pustule | raised well defined lesion containing pus |
| PUVA | psoralen plus Ultraviolet A |
| Vesicle | blister <5mm |
| Weal | transient lraised lesion with a pale centre and pink margin |
History & Exam
- How long has it been there?
- Does it hurt?
- Any other symptoms, eg itch?
- Any other lumps
- Is it getting bigger
- Otherwise well?
6S’s of skin lesions
- Site
- Size
- Shape
- Smoothness
- Surface
- Surroundings
- Does it tranilluminate?
- Fixed/tethered?
- Fluctuant/compressible?
- Temperature
- Tender?
- Pulsatile
| Intradermal | Subcutaneous |
|---|---|
| Sebaceous cyst | Lipoma |
| Abscess | Ganglion |
| Dermoid cyst | Neuroma |
| Granuloma | Lymph node |
| If a lump is intradermal you cannot draw the skin over it, while if the lump is subcutaneous, you should be able to manipulate it independently from the skin |
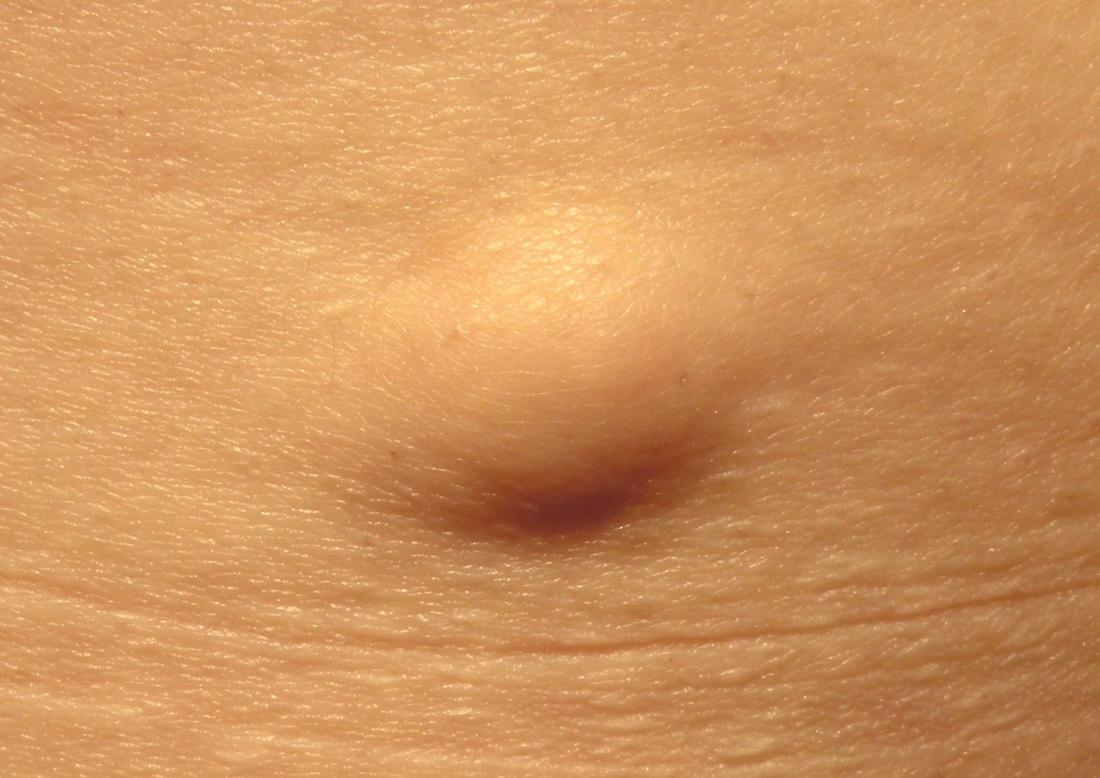
Lipomas
- Benign fatty lumps that occur wherever fat can expand (not scalp or palms)
- Smooth imprecise margins
- Slightly fluctuant
- Not fixed
- Symptoms usually due to pressure
- Very rarely malignant change
- Dercum’s disease - multiple scattered lipomas which may be painful - typically in post-menopausal women
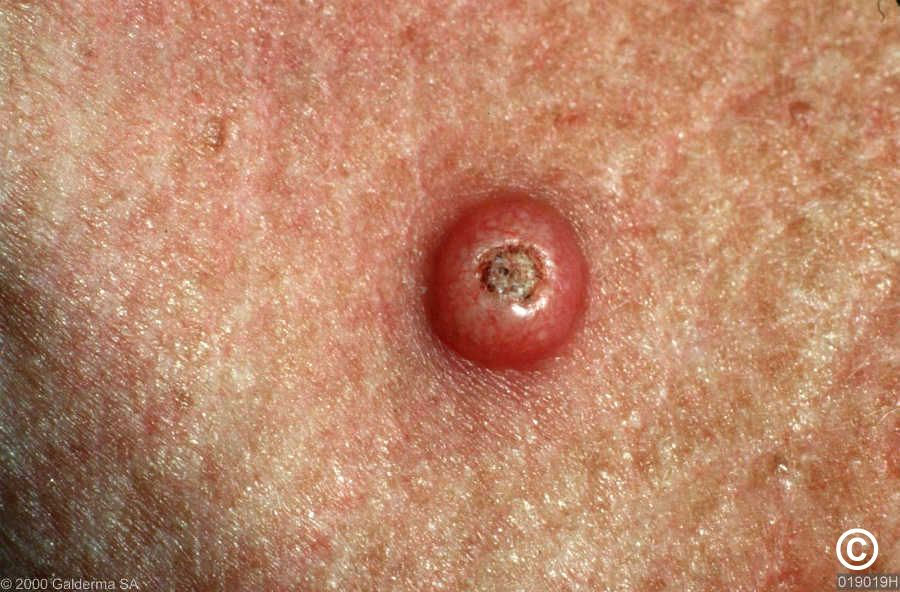
Sebaceous cysts
- Either epidermal or pilar cysts (not of sebaceous origin and contain keratin not sebum)
- Firm, round, mobile subcutaneous nodules of varying size
- Characteristic central punctum
- Infection common - pus exits through centre
- Treatment of bad ones is excision of cyst and contents
 Epidermal
Epidermal
Keratosis
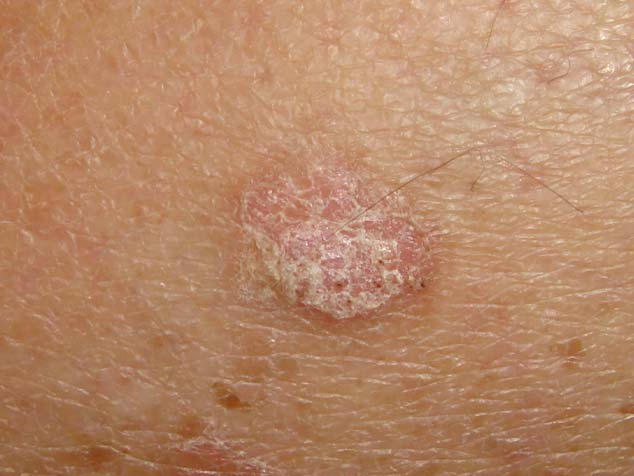
Solar (actinic) keratosis
- Sun-exposed skin sites
- Crumbly, yellow-white crusts
- Malignant change to Squamous cell carcinoma may occur after several years
- Cryotherapy, fluorouracil, imiquimod
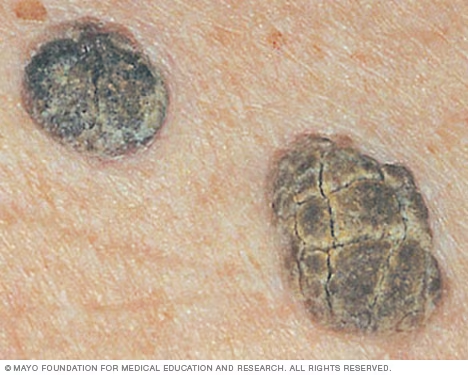
Seborrheic keratosis
- Looks scary but benign skin growth
- Look waxy or scaly and slightly raised. They appear gradually, usually on the face, neck, chest or back.
- Usually appear in numbers rather than a single lesion like in Melanoma
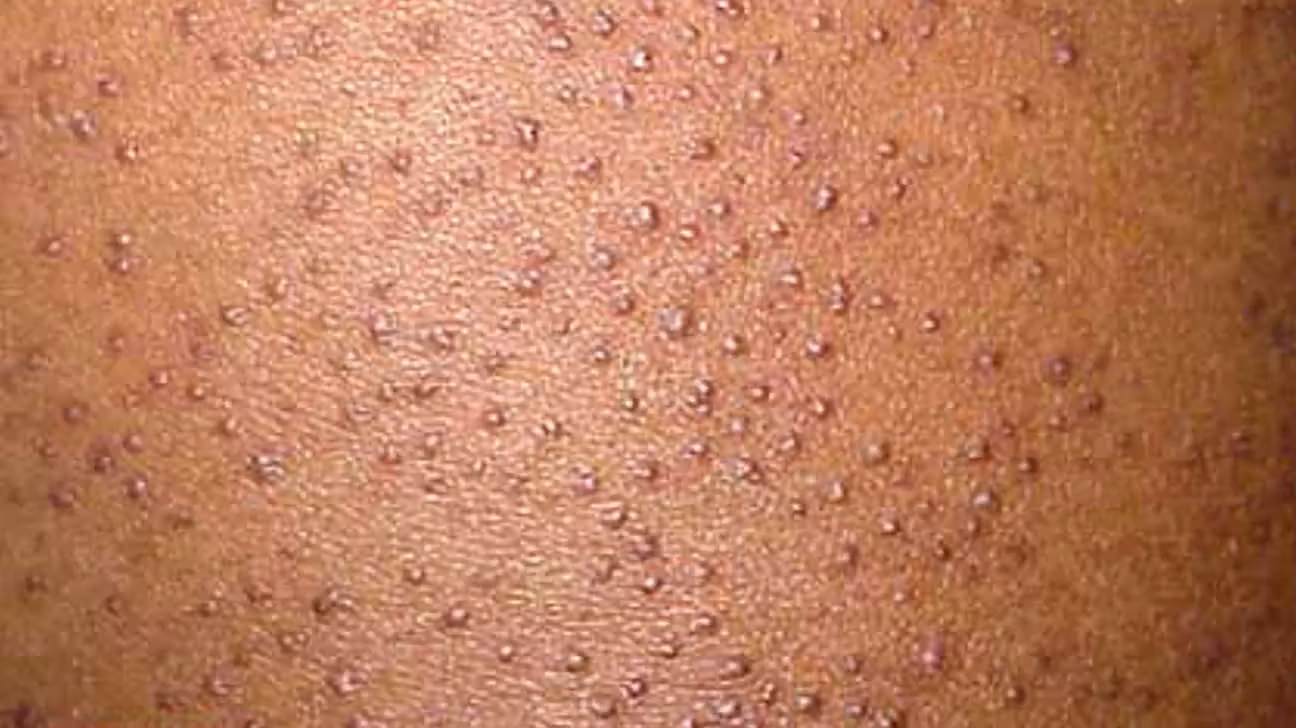
Keratosis pilaris
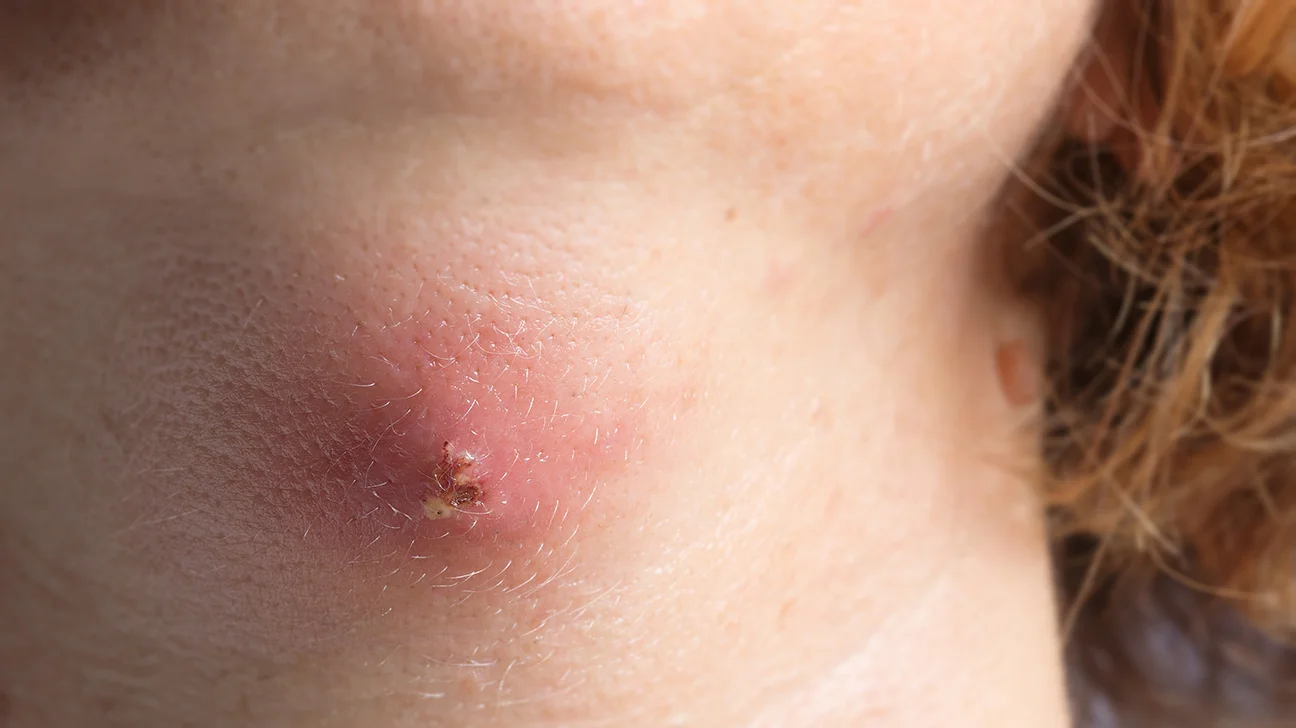
Cutaneous abscesses
- Staphylococci most common organism.
- Below the waist faecal organisms are common
- Treatment incise and drain
- Think Hidradenitis suppurativa if recurrent inguinal or axillary abscesses
Boils (furuncles)
- Abscesses involving hair follicle and associated glands
Carbuncle
- An area of subcutaneous necrosis which discharges itself on to the surface through multiple sinuses
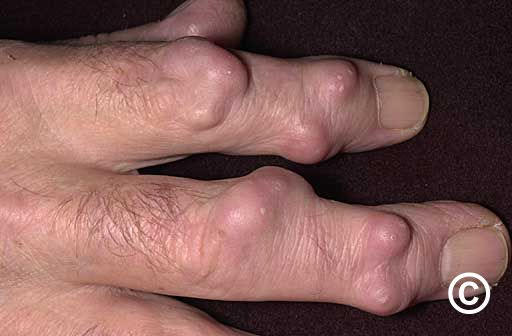
Rheumatoid nodules
- Collagenous granulomas which appear in established RA
- On the extensor aspects on the joints - esp elbows
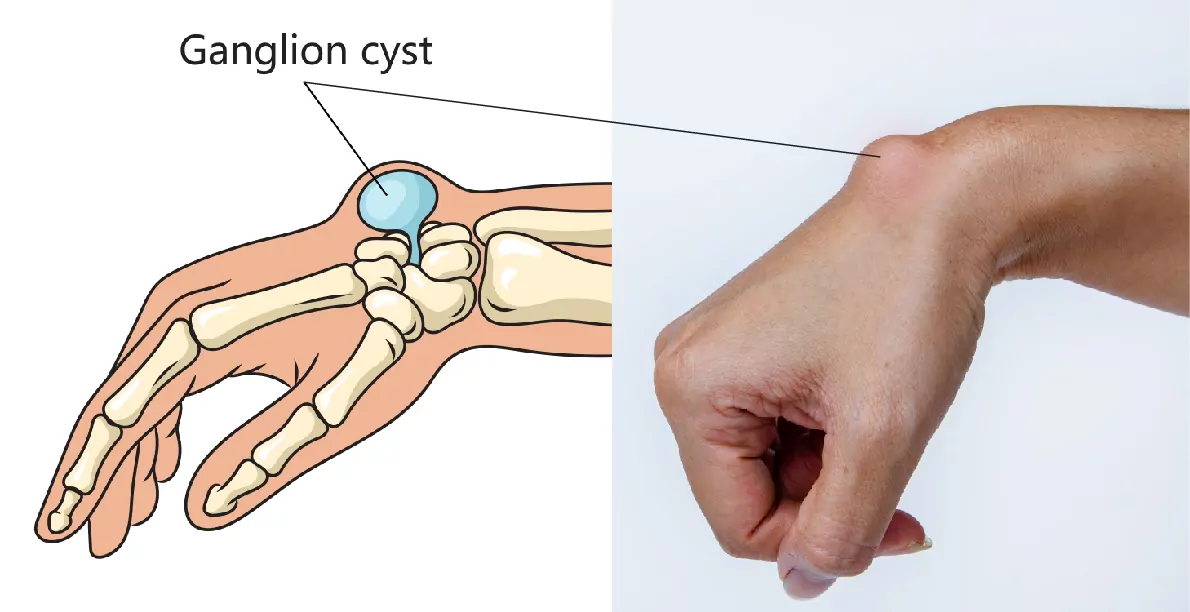
Ganglia
- Degenerative cysts from an adjacent joint or synovial sheath
- Commonly seeon on the dorsum of the wrist, hand or foot.
- May transilluminate
- 50% disappear spontaneously
- Bible smacker
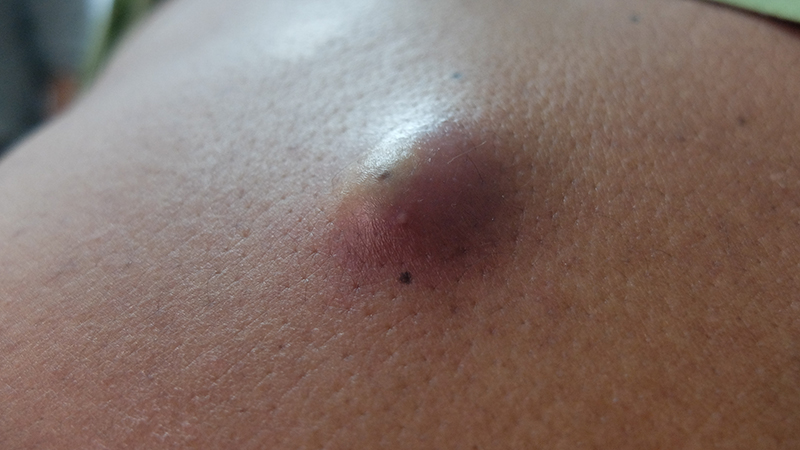
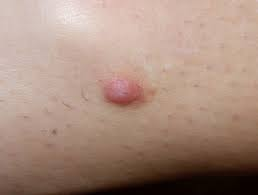
Dermatofibromas
- Can occur anywhere in body
- Most commonly under skin
- Whitish, benign tumour containing collagen, fibroblasts and fibrocytes
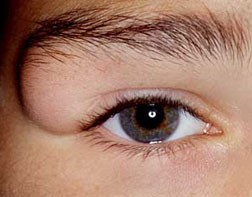
Dermoid cyst
- Contain dermal structures
- Found at junction of embryonic cutaneous boundaries eg midline or lateral to eye
Malignant tumours of connective tissues
- Fibrosarcoma, liposarcomas, leiomyosarcomas, rhabdomyosarcomas
- TNM grading
- Needle-core biopsies
- Refer to specialist
Neurofibromas
- Caused by Neurofibromatosis
- Autosomal dominant inheritance - expression of NF1 is variable even within a family
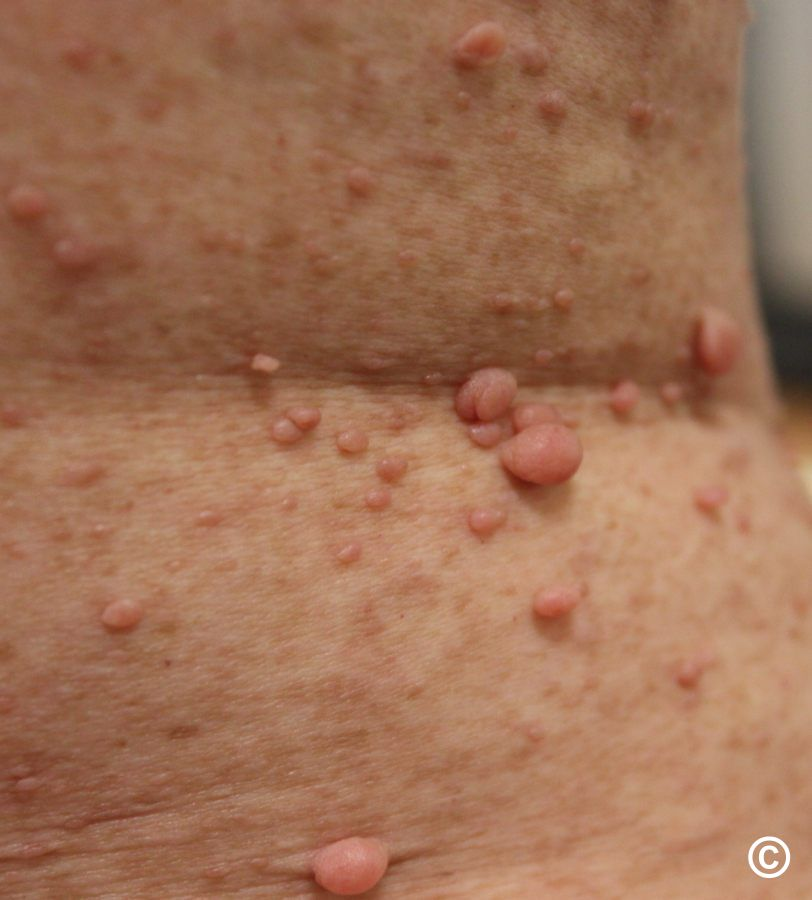
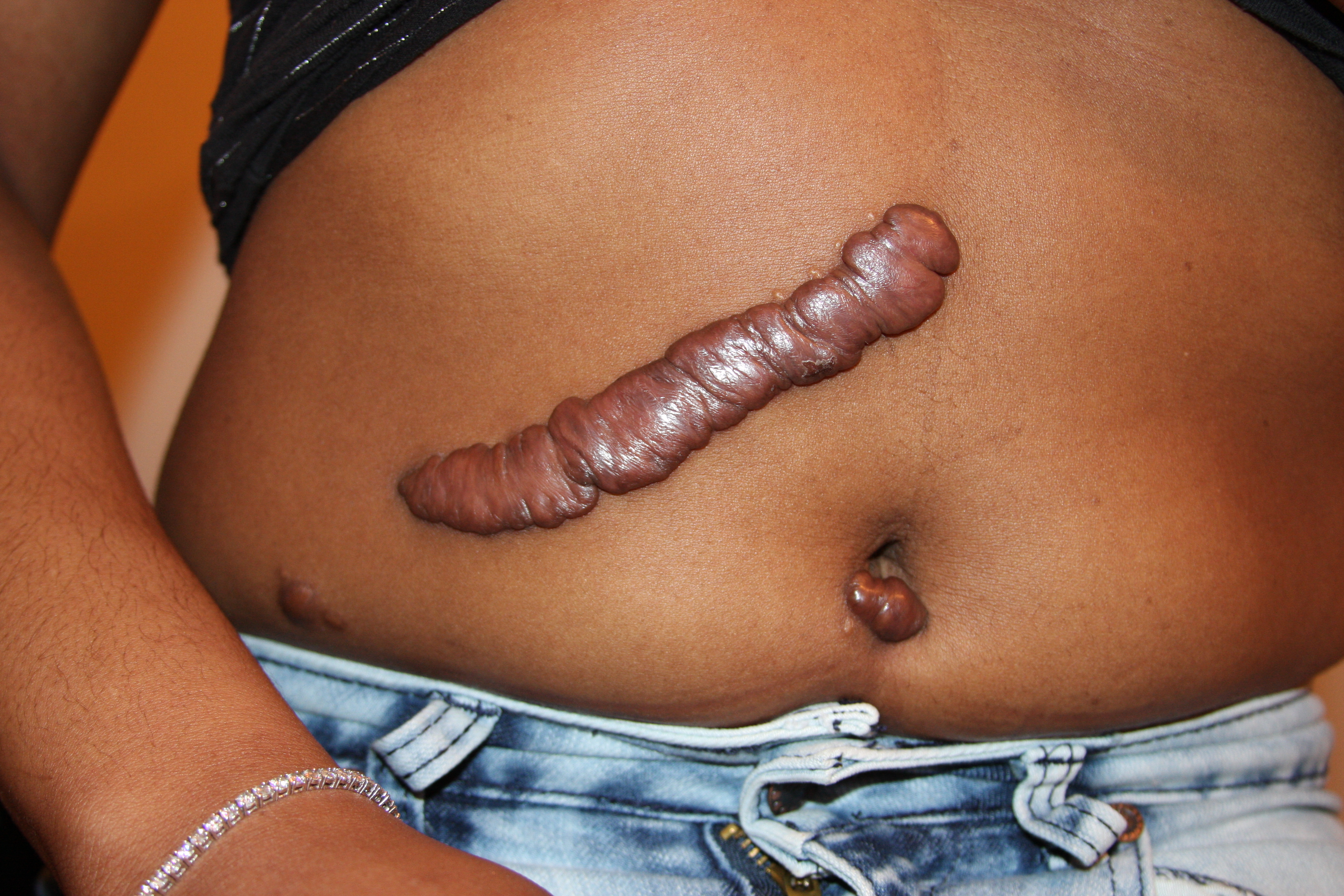
Keloids
- Irregular hypertrophy of vascularised collagen forming rainsed edges at sites of previous scars that extend outside the scar
- Common in dark skin
- Treatment can be difficult - intralesional steroid Injections
Keratoacanthomas
- Fast-growing benign, self-limitting papule plugged with keratin
- May be confused with Squamous cell carcinoma