Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that originates from pigment-producing cells called melanocytes. It is known for its potential to metastasize (spread) to other parts of the body, making early detection and treatment crucial. Melanoma is less common than other types of skin cancer but is more likely to become invasive and potentially life-threatening.
Superficial spreading melanomas (70%) - grow slowly and have a better prognosis than nodular melanomas
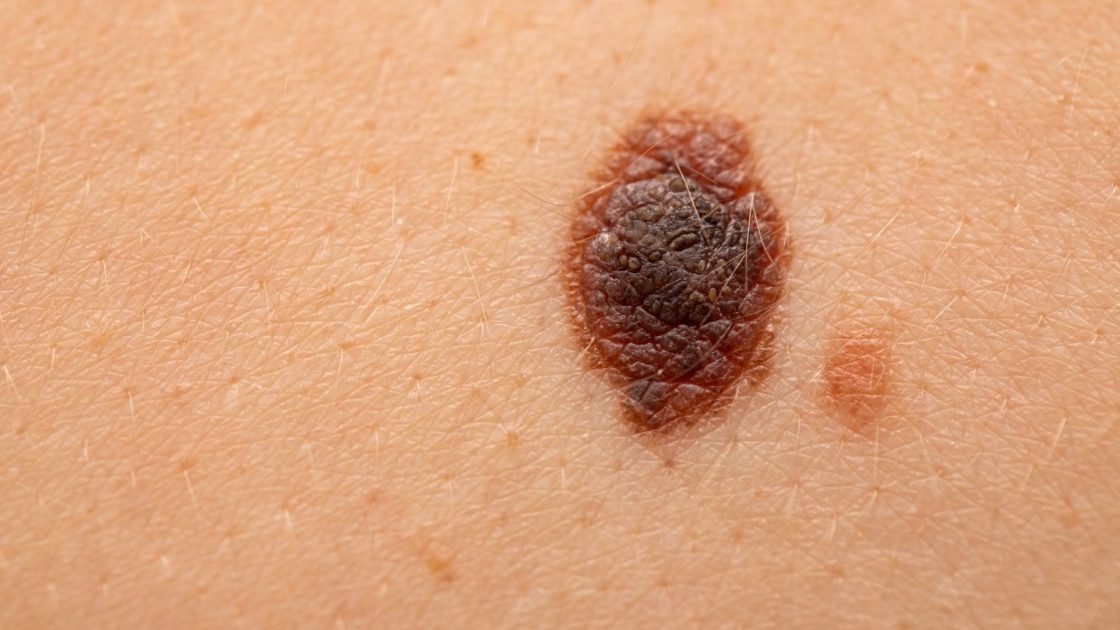
Nodular melanomas - grow vertically and invade deeply. They metastasise early
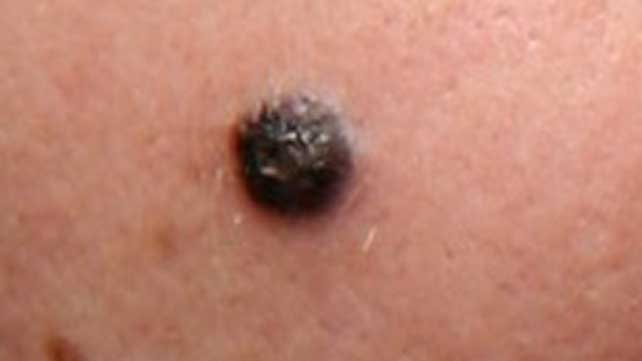
Causes/Factors
The primary cause of Melanoma is prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds - particularly in early years. Other risk factors include:
- Fair Skin: Light-skinned individuals are at a higher risk.
- History of Sunburns: Especially during childhood.
- Numerous Moles: Having many moles or unusual moles.
- Family History: A family history of melanoma increases the risk.
- Weakened Immune System: Due to conditions or medications.
Symptoms
- Changes in Moles: Changes in size, shape, color, or elevation of existing moles.
- New Moles: The appearance of new moles.
- Itching or Sensation: Moles that itch or cause a sensation.
Diagnostic Tests
ABCDE Criteria
- Asymmetry
- Border - irregular
- Colour - non-uniform
- Diameter - >7mm
- Elevated/Evolving
Management
Refer to specialist if >3 points or 1 point if suspicious:
| Major (2pts each) | Minor (1pt each) |
|---|---|
| Change in size | Inflammation |
| Change in shape | Sensory change |
| Change in colour | Diameter >7mm (unless growth is vertical) |
| Crusting or bleeding |
- Urgent Excision: Removal of the melanoma and a margin of healthy tissue.
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: Removal and examination of nearby lymph nodes.
- Immunotherapy: Ipilimumab blocks CTLA-4 (inhibitory T-cell receptor)
- Targeted Therapy: Medications that target specific genetic mutations in melanoma cells.
- Chemotherapy: In some cases, especially when melanoma has spread.
Complications/red Flags
- Metastasis: Melanoma can spread to other organs, making early detection crucial.
- Recurrence: Melanomas can recur, even after successful treatment.
- Lymph Node Involvement: Spread to nearby lymph nodes can occur.