- Cannabis is most common in 16-59 then cocaine and ecstasy
- But alcohol misuse is the fifth biggest risk factor for death across all ages
Basal ganglia, amygdala and prefrontal cortex are the regions most involved with addition - balance between glutamate, GABA and dopamine
Outpatient Counselling (addiction clinic), long-term therapeutic communities, etc
Alcohol
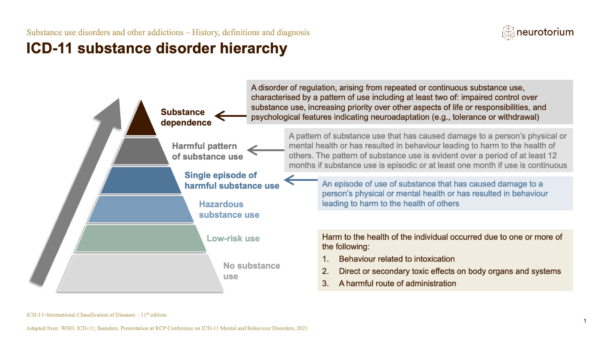
Anything up to 14 units a week spread over 3 days or more is okay. Need to differentiate from hazardous drinking, harmful drinking, and alcohol dependence.
- A common screening tool for alcohol misuse is the AUDIT-C questionnaire
- Main intervention is an alcohol detox. But this method can cause serious withdrawal symptoms - tremors, seizures, Delirium tremens. Can be deadly - needs to be carefully planned. Clordiazepoxideis often prescribed to help with symptoms
- Naltrexone is an opiate blocker that makes alcohol less enjoyable
- Acamprosate increases GABA and decreases excitatory glutamine thus reduces cravings - good side effect profile and well tolerated
- Disfiram causes unpleasant symptoms when drinking alcohol, nausea, vomiting, Arrhythmias. Contraindicated in patients with heart disease, psychosis and risk of suicide
Prophylactic oral thiamine should be given if they are malnourished or have liver disease
Opioid misuse
CNS depressants - overdoses can cause Respiratory Failure and death
- Main intervention if opioid detox with methadone reduction
- Alternative to this is buprenorphine reduction
- Counselling and rehab
Benzodiazepines
CNS depressants
Assisted withdrawal and supportive treatments
CNS stimulants
CNS stimulants activate the sympathetic nervous system which causes symptoms such as tachycardia, Essential hypertension, and mydriasis.
Patients using cocaine may develop tactile hallucinations and chest pain.
No specific drug treatment - supportive only managing withdrawal symptoms