Arrhythmias are:
- common
- often benign (but may reflect underlying cardiac disease)
- often intermittent
- occasionally severe
Causes/Factors
Cardiac
- Ischemic Heart Disease
- Structural changes
- Cardiomyopathy
- Pericarditis
- Myocarditis
Non-cardiac
- Caffine
- Smoking
- Alcohol
- pneumonia
- Drugs ( agonists, Digoxin, L-dopa, tricyclics)
- Metabolic imbalance (K, Ca, Mg, hypoxia, hypercapnia, acidosis, thyroid)
Presentation
- Palpitations
- Chest pain
- Presyncope/syncope
- Hypotension
- Pulmonary oedema
History
- Take a detailed history of papitations
- Ask SOCRATES basically
- Review drug history
- Ask about PMH + FH of cardiac disease or sudden death
- Syncope during exercise is always concerning
Diagnostic Tests
- Bloods - FBC, U&E, glucose, TSH
- ECG - ischaemic changes, PR interval, long QT, U Waves
- Possible 24h cardiac monitoring
Management
- Some can be managed conservatively e.g. reducing alcohol intake
- Drugs
- Pacemakers & ICDs
- Ablation
Regular rate tachycardias
See ECG Lead Placement & Interpretation for more
Narrow complex is atrial in origin (SVT) - broad complex is ventricular (VT)
Normal Conduction

Regular rhythm tachycardia
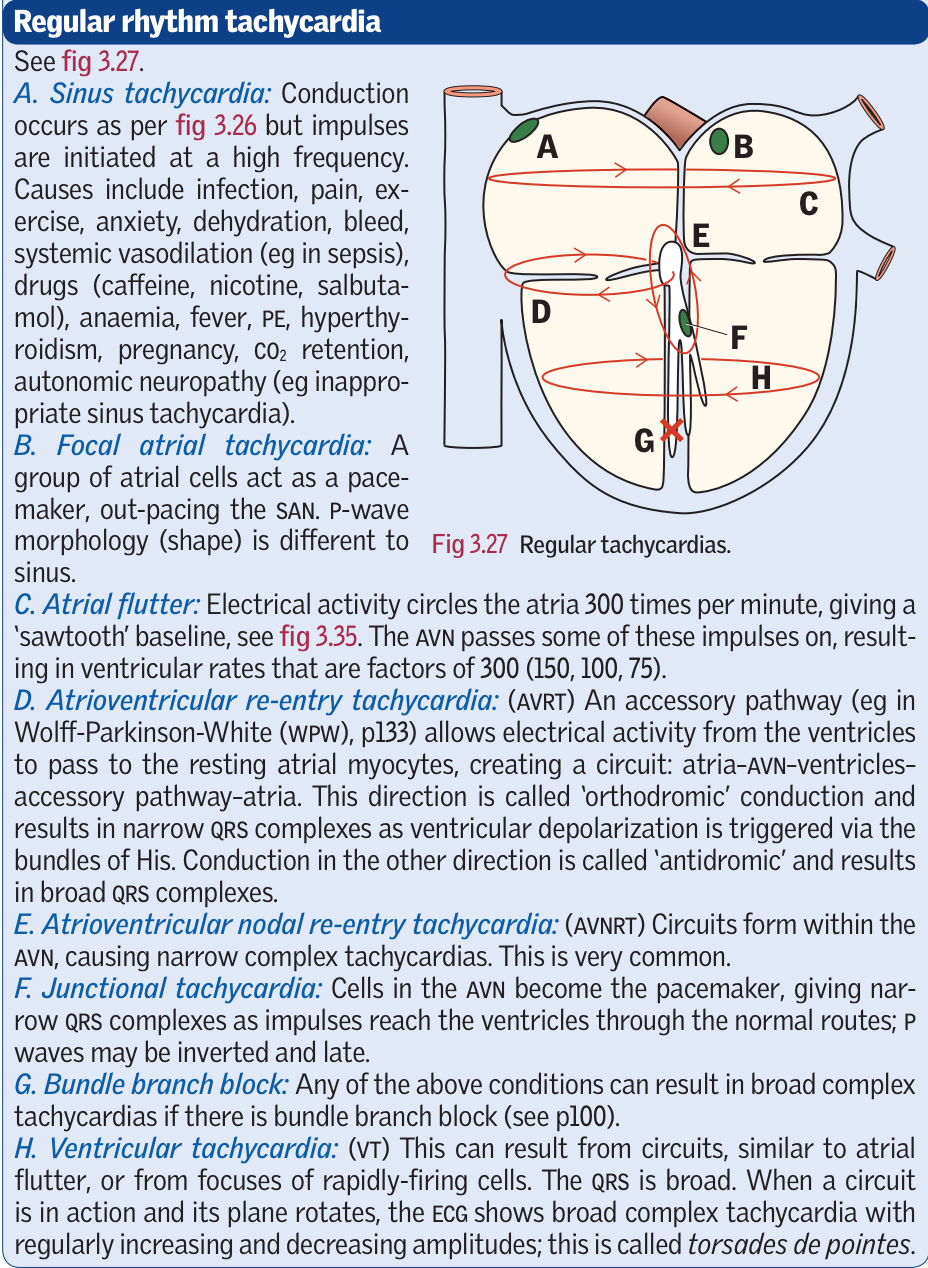
- Sinus tachycardia - from SAN - infection, pain, exercise, anxiety, dehydration, hypovolaemia
- Focal atrial tachycardia - a group of atrial cells act as a pacemaker out pacing the SAN - p wave morphology
- Atrial flutter - atrial activity cycles the atria at 300 bpm giving a sawtooth baseline. The AVN passes some of these impulses on giving ventricular creates that are factors of 300
- Atrioventricular re-entry tachycardia - accessory pathway (eg in WPW) allows electrical activity from the ventricles to pass to the resting atrial myocytes creating a circuit. ‘Orthodromic’ direction, results in narrow QRS. Conduction in the other direction is ‘antidromic’ and results in broad QRS (atrial trigger ventricular contraction not via bundle of His)
- Atrioventricular nodal re-entry - circuits form within the AVN causing narrow complex tachycardias
- Junctional tachycardia - cells in AVN become pacemaker giving narrow QRS complexes. p waves may be inverted or late
- Bundle Branch Block - any of the conditions above can result in a broad complex tachycardia if there is a BBB
- VT - Similar to atrial flutter circuits - broad QRS. The plane of the circuit can rotate when in action seen as increasing and decreasing amplitude - torsades de pointes