Carcinoma of the bronchus - second most common cancer in UK, only 5% cured
Primary lung tumours
- 90% are carcinomas
- Non-small cell carcinoma 85%
- adenocarcinoma 30% - mucin production
- Squamous cell carcinoma 20% - presence of keratinization
- large cell carcinoma 10%
- Small cell 15% - arise from endocrine cells → excrete peptides → Paraneoplastic Syndromes
Main morphological difference between the two is nuclear characteristics and amount of cytoplasm. Small cell “always” smoking
Secondary Lung Tumours
- More common than primary
- Multiple discrete nodules
- Most commonly from breast, GIT, kidney
- Sarcomas
- Melanomas
- Lymphomas
Causes/Factors
- Smoking (90%)
- asbestos
- chromium
- arsenic
- iron oxides
- radon gas
Symptoms
- cough
- haemoptysis
- dyspnoea
- chest pain
- weight loss
Small cell
-
ADH
-
ACTH - not typical, Essential hypertension, hyperglycaemia, hypokalaemia, alkalosis and muscle weakness are more common than buffalo hump etc
Squamous cell
-
parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTH-rp) secretion causing Hypercalcaemia
-
hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy (HPOA)
-
Hyperthyroidism due to ectopic TSH
Adenocarcinoma
- gynaecomastia
- hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy (HPOA)
Signs
- clubbing of fingers
- Anaemia
- Pleural Effusion
- hepatomegaly
- metastasis - lymphadenopathy
Diagnostic Tests
- Made on histology (biopsy)
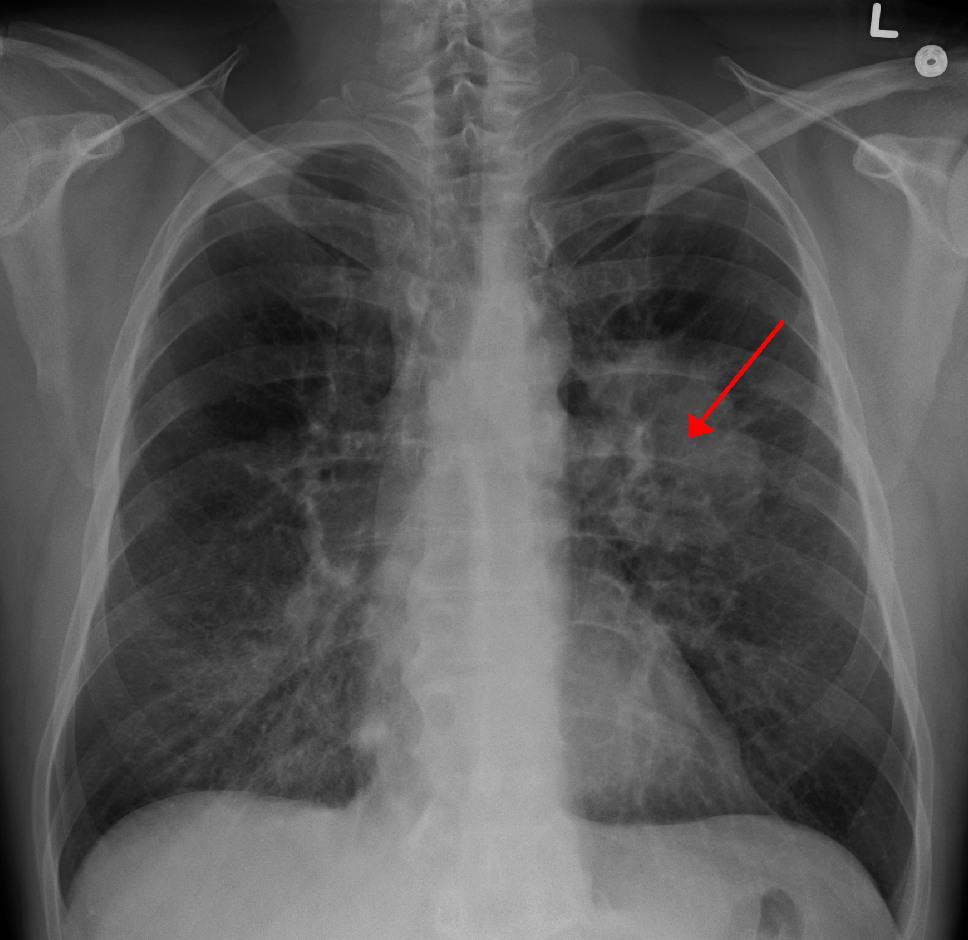
- Can see tumour of CXR
Management
- Pemetrexed + (cisplatin) chemotherapy
- Surgery hard to evaluate
- Radiotherapy controversial
Complications/red Flags
Poor prognosis in general
- phrenic + recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy (mass impinges)