- Lack of dopamine
- Symptoms begin when 80% of dopamine producing cells (substantia nigra) have died
Parkinsonism is anything that brings about these symptoms. Parkinson’s is the progressive disease - most common cause of Parkinsonism
Causes/Factors
-
FH
-
Male
-
Head injury
-
Pesticide exposure (maybe)
-
Drug induced (anti-psychotic drugs) - reduce dopamine e.g. risperidone, haloperidol, Metoclopramide promethazine, prochlorperazine
Decrease risk
- Smoking
- Coffee
- NSAIDs
- Estrogen replacement
Symptoms
-
Parkinson’s Dementia (Lewy Body)
-
Micrographia
-
Sleep disorders - REM sleep disturbance, presents up to 30 years before Parkinson’s
-
Postural hypotension
-
Urinary problems
-
Loss of smell
-
Hypersalivation
Signs
TRAP features
- Tremor - pill rolling tremor - resting
- Rigidity
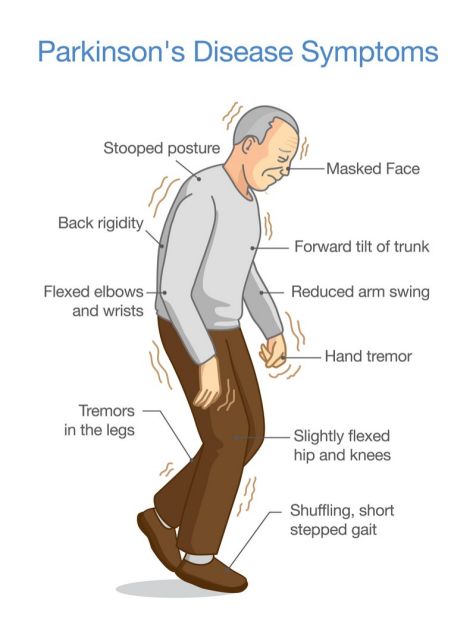
- Akinesia/bradykinesia - reduced blink, face expression, soft voice, shuffling steps, reduced arm swing. Trouble getting out of chair
- Postural changes (imbalance, falls)
Diagnostic Tests
Diagnosis of exclusion - clinical diagnosis so just need to rule out other causes
- MRI
- Blood tests
- No specific medical test
- Referral to movement clinical before medicating
Management
If too much dopamine is replaced, can cause frontal changes in patients. Need to be given at a specific time of day every day. Sudden withdrawal can cause life threatening symptoms.
- Levadopa - precursor of dopamine that passes through the BBB + peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor (Carbidopa). Reduces peripheral side effects by stopping its breakdown into dopamine
- Dopamine
- MAO-B inhibitors
- Amantadine
- COMT inhibitors
Pallidotomy (outdated) - probe inserted into globus pallidus and frozen to eliminate dyskinesia
Deep brain stimulation - electrodes placed in important areas of the brain and pulses are generated from a device under the skin in chest
Complications/red Flags
The resting tremor may take longer than the other symptoms to improve after medicating