SAMPLE History Whilst Assessing Airway
- Signs and symptoms
- Allergies
- Medications
- Past medical history
- Last oral intake
- Events surround injury/illness
Acute Coronary Syndrome
- Don’t forget troponin
STEMI
- MOAN - morphine 5-10mg, oxygen 100%, aspirin 300mg & ticagrelor 180mg, nitrates GTN spray (metoclopramide 10mg)
- PCI within 2 hours - if not possible thrombolysis with Fondaparinux
NSTEMI
- MOAN - morphine 5-10mg, oxygen 100%, aspirin 300mg, nitrates GTN spray (metoclopramide 10mg)
- Thrombolyse with LMWH - subcut as per local guidelines
High Risk on GRACE Score
- Fondaparinux (cannot give if immediate angiography)
- If Clinically Unstable: Immediate angiography. If Stable (not bleeding): Angiography within 72 hours (with follow-on PCI if indicated)
- Not on anticoagulation: Prasugrel/Ticagrelor + Aspirin - Only give prasugrel once PCI intended
- On previous Anticoagulation: Clopidogrel + Aspirin.
Low Risk on GRACE Score
- Fondaparinux
- Low Bleeding Risk: Ticagrelor + Aspirin
Higher Bleeding Risk: Clopidogrel + Aspirin
Exacerbation of Heart Failure
Acute problems caused by pulmonary oedema
- Troponin and BNP
- IV furosemide 20-40mg
- Do not offer: nitrates or opiates
- Conside CPAP
Exacerbation of COPD
H. influenzae most common organism.
- Give oxygen to meet requirements but take early ABG to identify retainers. Eg 28% Venturi mask at 4 l/min if risk/features of hypercapnia
- Salbutamol 5mg neb - back to back
- Ipratropium bromide 500 micrograms 4-6 hourly
- 40mg oral pred or IV hydrocortosone 100mg.
- IV theophylline may be considered.
Acute Kidney Injury
STOP AKI
- Sepsis - complete 6 if suspected cause of AKI
- Toxins - gentamicin, NSADs, iodine contrast
- Optimise - blood pressure and volume status
- Prevent - treat complications - acidosis, hyperkalaemia, pulmonary oedema
Monitor fluid balance
Asthma
- <33% of predicted or best, < 92% ORA < 8kPa life PEFR life-threatening.
- Confusion automatically means life threatening.
- Raised is near fatal
- Oxygen 100%.
- 5mg back to back salbutamol nebs ± ipratropium (if no response to salbutamol).
- Prednisolone 40mg oral or IV hydrocortisone 100mg
- Consider magnesium sulphate
Oh
Shit,
I
Hate
My
Asthma
- Oxygen
- Salbutamol nebulisers
- Ipratropium bromide nebulisers
- Hydrocortisone IV or Oral Prednisolone
- Magnesium Sulfate IV
- Aminophylline / IV salbutamol
Patients after an exacerbation can be discharged after:
- been stable on their discharge medication (i.e. no nebulisers or oxygen) for 12-24 hours
- inhaler technique checked and recorded
- PEF >75% of best or predicted
Anaphylaxis
- Maintain airway
- IV fluid challenge
IM adrenaline - 1:1000 repeat every 5 minutes
| Group | Dose |
|---|---|
| Adults (12+) | 500 micrograms |
| Children (6-12) | 300 micrograms |
| Children (<6) | 150 micrograms |
Arrhythmias
Only if things are “adverse”
Bradycardias
- IV atropine 500 micrograms - repeat up to 3mg
- or transcutaneous pacing
- Get a pace maker fitted asap
Tachycardias
Tip
‘Amiodarone’ is broader than ‘Adenosine’
Give amiodarone in broad complex tachy and Adenosine in narrow complex tachy
Supraventricular tachycardia
- Vagal/valsalva manoeuvers
- If they don’t work IV adenosine
Broad complex tachycardia
- DC cardioversion
- IV amiodarone if adverse features not present
Polymorphic ventricular tachardia
- Subtype of this is torsades de pointes - precipitated by prolongation of the QT interval
- IV magnesium
CPR
-
DRS ABC
-
100-120 BPM 5-6cm depth
-
30:2 CPR:Rescue breaths in adults
-
Switch person every 2 minutes
-
If in VF/ pulseless VT give 1 shock followed by 2 mins of CPR
-
If the arrest was witnessed give up to 3 shocks before starting CPR
-
Adrenaline 1mg immediately in non-shockable rhythms
-
In VF/pulseless VT give adrenaline once CPR have restarted after 3rd shock
-
Repeat adrenaline every 3-5 minutes whilst ALS continues
-
Give 300mg amiodarone after 3 shocks then 150mg (ideally through a central line)
Reversible causes of cardiac arrest:
| The ‘Hs’ | The ‘Ts’ |
|---|---|
| - Hypoxia - Hypovolaemia - Hyperkalaemia, hypokalaemia, Hypoglycaemia, Hypocalcaemia, acidaemia and other metabolic disorders - Hypothermia | - Thrombosis (coronary or pulmonary) - Tension pneumothorax - Tamponade - cardiac - Toxins |
Delirium
Cause:
-
Pain
-
Infection
-
Nutrition
-
Constipation
-
Hydration
-
Medication
-
Environment/electrolytes
Consider Sepsis 6
If a danger to themselves or others:
- Haloperidol 1st line - contraindicated in those with prolonged QTc, ventricular arrythmias or Parkinson’s disease
- Lorazepam 2nd line
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Metabolic acidosis with Anion gap
- Raised blood glucose >11 mmol/L
- Capillary ketones >3 mmol/L
- Venous pH <7.3 or bicarb <15 mmol/L
Management:
- Fixed rate insulin infusion 0.1 units/kg/hour
- Continue long acting insulin - short acting insulin should be stopped
- Repeat IV fluids 1L 0.9 NaCl over 1hr - add potassium as required. Most patients with DKA are deplete around 5-8 litres
- Potassium cannot be given faster than 20mmol/hour
- Once blood glucose is <14 mmol/L add an infusion of 10% dextrose
GI Bleed
Fluid resuscitation:
-
Fluid challenge of 500ml over 15 minutes
-
Aim not to over fill due to increased bleeding with higher pressure
-
If massive haemorrhage - active Major haemorrhage protocol calling blood bank.
- 4 units of RBC and 4 units of FFP 1:1 transfusion ratio
- Consider TXA
- Correct any clotting abnormalities
- If bleed from varices patient needs terlipressin and prophylaxic antibiotics
-
Urgent OGD once resusitated
Head Trauma
-
worst and first/thunderclap Subarachnoid haemorrhage.
-
N&V - 2 or more episodes of vomiting urgent head CT
-
Panda eye - basal skull fracture
-
Cushing’s triad of signs brain herniation
- Cheyne-Stokes breathing
- Hypertension
- Bradycardia
-
Correct any coagulopathies
-
Refer to neurosurgery esp if ICP
Hyperkalaemia
Causes
-
K sparing diruetics - amiloride, spiro
-
ACEi
-
NSAIDs
-
Rhabdomyolysis
-
Metabolic acidosis
-
Mild - K+ 5.5 - 5.9 mmol/L
-
Moderate - K+ 6.0 - 6.4 mmol/L
-
Severe - K+ ≥ 6.5 mmol/L
ECG changes:
- Tall tented T waves
- loss of P waves
- broad QRS
All patients with severe hyperkalaemia or with ECG changes should have emergency treatment:
- IV calcium gluconate - stabilise myocardium
- Insulin/dextrose infusion - shift potassium into cells
- Other - salbutamol nebs
Pneumonia
CURB-65 - one point for each
- Confusion - AMTS 8
- Urea - >7 mmol/L
- RR - 30
- Blood pressure < 90 systolic or <60 diastolic
- Age 65 (soft score)
Management 0-1 - low risk home management - 500mg amoxicillin TDS for 5 days 2 - intermediate risk - short in-patient stay 3 - high risk - severe pneumonia
Broad spectrum antibiotics empirically - co-amoxiclav or ceftriaxone plus marcolide (clarythromycin)
Poisoning
Opioid
- Pin point pupils
- N&V
- Reduced GCS
- Bradycardia
- Reduced RR
Naloxone - repeat doses or infusions may be required as cleared faster than opioids
Benzodiazepines
- Pale
- Clammy
- Cool peripheries
- Confused
- Unsteady gait
- Reduced RR
Flumazernil used to reverse - sudden withdrawal may causes seizures arrhythmias and hypotension
Tricyclic anti-depressants
TCA examples: amitriptyline, clomipramine, dosulepin, imipramine, lofepramine and nortriptyline
- Dilated pupils
- Fever
- Dry skin
- Urinary retention
- Widening QRS
Give sodium bicarbonate - cardioprotective + lowers amount of active form of the drug
Paracetamol
- RUQ pain
- Jaundice
- Deranged LFTs
-
- ↑ AST
- ↑ PT and INR
- normal ALP and other factors not for hepatocyte damage
-
- Coagulopathic
- Renal failure ↑ creatinine
- Lactic acidosis
Management
Immediate to <1 hour since ingestion: Activated charcoal to prevent absorption into the bloodstream
1 to 8 hours: Plot paracetamol concentration on concentration curve and determine if N-acetylcystine is required
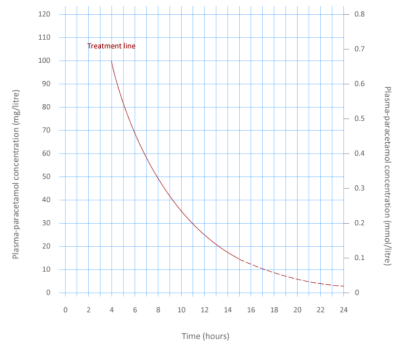
8-24 hours: Calculate weight and start N-acetylcysteine if ingestion is > 150 mg/kg (or if Paracetamol concentration is not available).
24 hours+: Start N-acetylcystine or any time if they are clearly jaundiced or have hepatic tenderness, their ALT is above the upper limit of normal
Unsure or staggered overdose: Always give N-acetylcystine if unsure of the timeline or if there was more than 1 hour between taking all of the tablets
pulmonary embolism
Calculate risk with Well’s Score
- Fracture of Lower limb
- HF/AF
- Surgery/trauma
- OCP
- Pregnancy etc
Non-specific signs:
- Tachypnoeic
- Low SpO2
- Tachycardic
- Hypotensive
- Raised JVP
Management
-
Well’s 4+ perform a CTPA or alternative
-
<4 perform a D-dimer and if positive get a CTPA
-
DOAC - apixaban or rivaroxaban first line
-
LMWH main alternative (e.g. in Kidney Failure patients)
Pneumothorax
- Iatrogenic
- Trauma
- Ventilated patients
Deviated trachea with absence breath sounds & reduced chest expansion. Chest XR
Management:
- Needle decompression (large bore cannula in 4th or 5th intercostal space anterior to mid axillary line just superior to following rib - NOT INFERIOR)
Sepsis
- Blood cultures
- Urine output - monitor hourly, U&Es, urine culture
- Fluid resuscitation 500ml over 15 minutes
- Antibiotics IV broad spec - LTHT guidelines (tazocin 4.5 g every 8 hours; increased if necessary to 4.5 g every 6 hours)
- Lactate measurement - from arterial or venous blood gas
- Oxygen to correct hypoxia
Status Epilepticus
- Alcoholism
- Drug use
- Hypoxic episodes
- Space occupying lesions
- Trauma
- Metabolic causes
Different classifications:
- Generalised tonic-clonic
- Focal - isolated muscle group twitching with intact consciousness
- Non-convulsive - impaired awareness, absence, aware
Difficult to obtain obs
Management
- IV lorazepam 0.1mg/kg - may be repeated once after 5-10 minutes
- If status is ongoing can give second line agent - levetiracetam, Phenytoin or sodium valporate
- Consider IV thiamine and glucose for Alcoholism
- If refractory status (45 minutes from onset) RSI with anaesthesiologist
Ischaemic Stroke
- Aspirin 300mg - as soon as hemorrhagic been excluded
- Within 4.5hr = thrombectomy + thrombolysis (alteplase)
- Within 6-24hrs = thrombectomy only
- Wake up Stroke (unknown) = thrombectomy only
Discharge medications
- Dual antiplatelet - 2 weeks 300mg then Aspirin 75mg + Clopidogrel 180mg
- ACE inhibitor - reduce blood pressure
- Beta blocker - reduce blood pressure
- Statin 80mg