More PTH increases serum calcium
Symptoms from hypercalcaeimia: moans, groans, stones, and bones
Polydipsia, polyuria and Essential hypertension are common too. Other important associations are renal stones and pancreatitis.
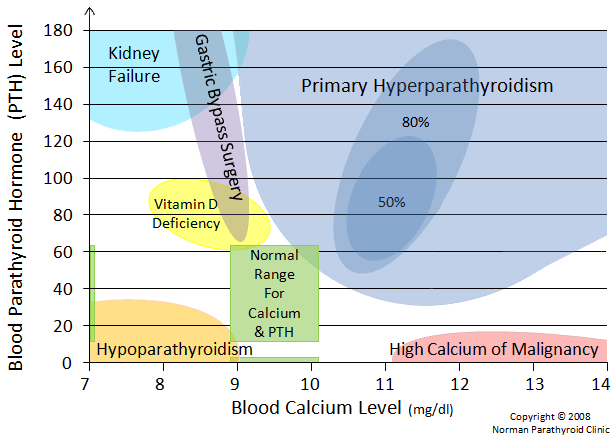
Primary
Increased PTH, increased calcium
- Uncontrolled parathyroid hormone production by a tumour of the parathyroid gland - leading to Hypercalcaemia
- Treatment is to remove the tumour surgically
Secondary
Low calcium, increased PTH
- Insufficient vitamin D or kidney disease reduces calcium absorption from the intestines, kidneys and bones
- Results in a low blood calcium
- The parathyroid glands are correctly reacting to the low calcium
- Treatment is to correct the underlying vitamin D deficiency or Chronic Kidney Disease
Tertiary
Increased calcium, increased PTH
- Gland hyperplasia from chronic secondary hyperparathyroidism
- With recent treatment of vitamin D replacement