- Abnormalities of kidney function or structure present on at least 2 occasions >3 months apart.
- Unlikely to be reversible
- CKD replaces the term chronic renal failure.
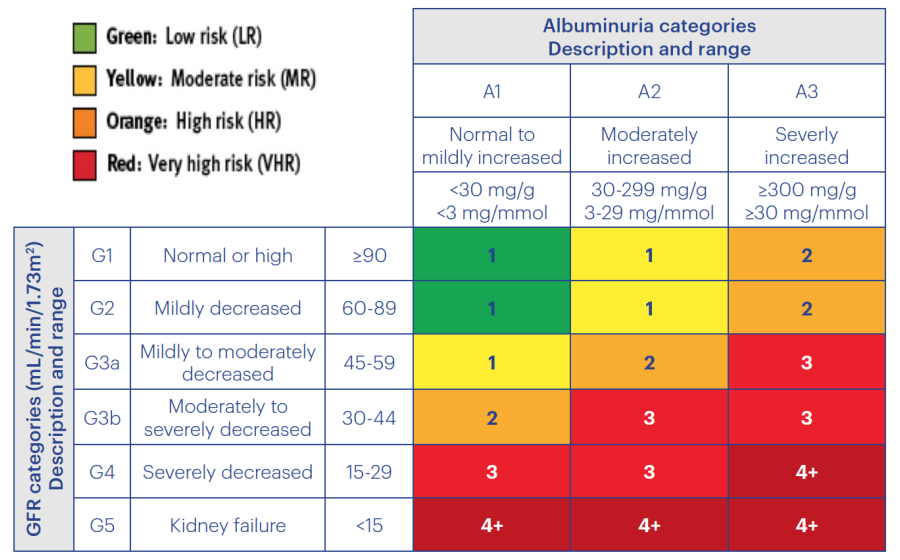
5 Stages dependent upon eGFR and albumin/creatine ratio (ACR)
Causes/Factors
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Hypertension
- Age 75+
- Glomerulonephritis
- Obstruction of kidney (without acute effect)
- Polycystic Kidney Disease
- Alport Syndrome
- APOL 1 Gene
- Acute Kidney Injury
- Reflux Nephropathy
- Chronic nephrotoxin use
Symptoms
-
Silent disease
-
May not manifest until significant decrease in kidney function
-
Reduced urine output
-
Aches and pains
-
Salt and water retention
-
Loss of lean body mass-muscle weakness
-
Vomiting etc
Diagnostic Tests
- Bloods - eGFR
- Urinalysis - blood/protein uACR annually
- BP
Distinguish between AKI and CKD: baseline creatinine value. Favouring CKD:
- Anaemia
- low calcium
- high phosphate
- elevated parathroid hormone
- Ultrasound appearances
Management
- Change life style to reduce risk
- Tolvaptan (for Polycystic Kidney Disease)
Kidney Replacement Therapy
- Haemodialysis
- Peritoneal Dialysis
- Transplantation
Palliative Care sometimes as its a lot of effort to continue with dialysis
- SGLT 2 Inhibitors
- reduces declining kidney function
- reduces risk of end stage kidney disease
- Or dying from causes related to the kidneys or cardiovascular system
- Ongoing studies to evaluate in patients with CKD without diabetes
Complications/red Flags
- Increased risk of other outcomes
- Coronary Artery Disease
- Acute Kidney Injury
- Hyperparathyroidism (low Ca, low activated vit D, high phosphate causes increased PTH )
- Anaemia
- Essential hypertension