Previously known as acute renal failure. Usually doesn’t occur in isolation
Stages
| Stage | Creatinine | Urine Output |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SCr increase >26 mol/L within 48hr or SCr increase 1.5-1.9x baseline | <0.5mL/kg/hr for 6 hours |
| 2 | SCr 2-2.9x increase from baseline | <0.5mL/kg/hr for 12 hours |
| 3 | SCr 3x increase etc, SCr increase 354, initiated on RRT | <0.3mL/kg/hr for 24 hrs |
Causes/Factors
Lots of risk factors like age 75+, Diabetes Mellitus, Heart Failure, etc
Pre-renal - something causes BP
- vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Diuretics
- Haemorrhage
- Burns
- Renal Artery Stenosis
Intrinsic - something within the kidney
- NSAIDS
- Nephrotoxins
- Glomerulonephritis
- Vascular
Post-renal
- Kidney stones
- Tumours
- Retroperitoneal fibrosis
Clinical Presentation
- AKI is usually a silent disease
- Possibly kidney stones
- Always suspect in acute patients with risk factors
Diagnostic Tests
- FBC, U&E and bicarbonate, C reactive protein (CRP), LFTs
- Calcium & phosphate
- Creatine kinase
- Urinalysis
- Ultrasound if suspected obstruction
- Biopsy
Management
- Manage underlying cause of AKI
- Supportive - renal (kidney) replacement therapy
- hyperkalaemia - non-responsive to medicine
- pH <7.1
- high urea
Complications/red Flags
Refractory Hyperkalaemia
- Leads to tented T-wave
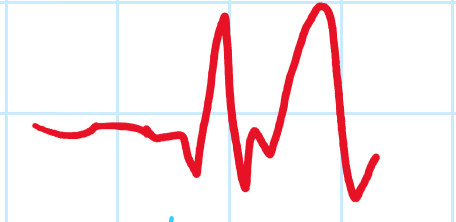
- Give calcium gluconate → protects heart and buys time, glucose/dextrose + Insulin and possible Salbutamol nebuliser
Acidosis
Uraemic symptoms
- nausea
- pruritis
- malaise
Therapy-resistant fluid overload